Etiology
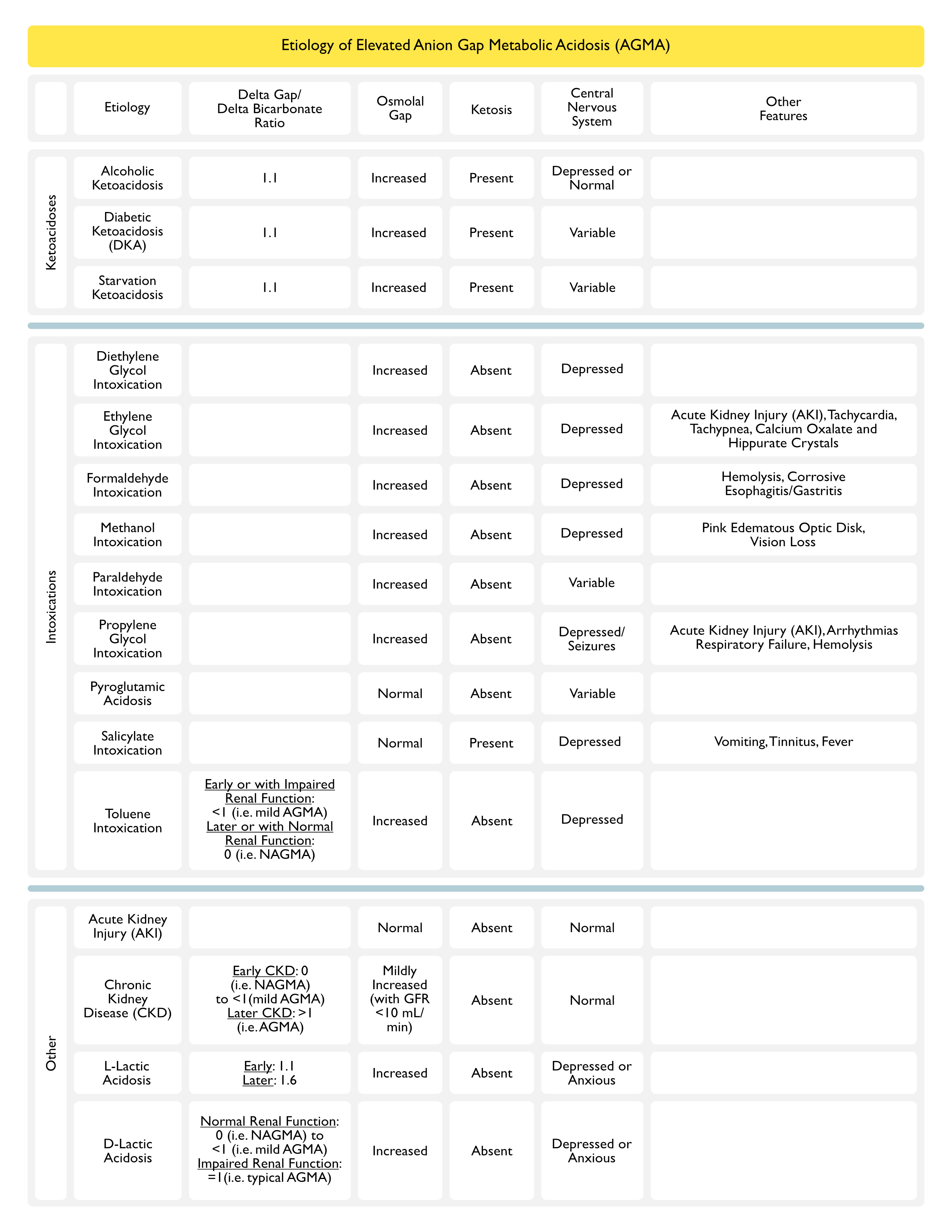
Ketoacidoses
- Alcoholic Ketoacidosis (AKA) (see Alcoholic Ketoacidosis and Ethanol)
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) (see Diabetic Ketoacidosis and Hyperosmolar Hyperglycemic State)
- Starvation Ketoacidosis (see Starvation Ketoacidosis)
Intoxications
- Diethylene Glycol Intoxication (see Diethylene Glycol)
- Ethylene Glycol Intoxication (see Ethylene Glycol)
- Formaldehyde Intoxication (see Formaldehyde)
- Methanol Intoxication (see Methanol)
- Paraladehyde Intoxication (see Paraldehyde)
- Propylene Glycol Intoxication (see Propylene Glycol)
- Pyroglutamic Acidosis (PCA, Pidolic Acid, Pyroglutamate, 5-Oxoproline) (see Pyroglutamic Acidosis)
- Salicylate Intoxication (see Salicylates)
- Toluene Intoxication (see Toluene)
Other
- Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) (see Acute Kidney Injury)
- Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) (see Chronic Kidney Disease)
- Lactic Acidosis (see Lactic Acidosis)
Etiology (GOLDMARK Mnemonic)
- G: Glycols
- Diethylene Glycol Intoxication (see Diethylene Glycol)
- Ethylene Glycol Intoxication (see Ethylene Glycol)
- Propylene Glycol Intoxication (see Propylene Glycol)
- O: 5-Oxoproline (Pyroglutamic Acid) (see Pyroglutamic Acidosis)
- L: L-Lactic Acid (see Lactic Acidosis)
- D: D-Lactic Acid (see Lactic Acidosis)
- M: Methanol (see Methanol)
- A: Aspirin (see Salicylates)
- R: Renal Failure
- Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) (see Acute Kidney Injury)
- Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) (see Chronic Kidney Disease)
- K: Ketoacidosis
- Alcoholic Ketoacidosis (AKA) (see Alcoholic Ketoacidosis)
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) (see Diabetic Ketoacidosis and Hyperosmolar Hyperglycemic State)
- Starvation Ketoacidosis (see Starvation Ketoacidosis)
Diagnosis
Serum Chemistry
- Serum Bicarbonate: decreased
Serum Anion Gap (see Serum Anion Gap)
- Elevated
Arterial Blood Gas (ABG) (see Arterial Blood Gas)
- Decreased Serum Bicarbonate with Respiratory Compensation: assessment of the appropriateness of respiratory compensation can be determined using standard rules of expected compensation (see Acid-Base Physiology)
Serum Osmolality (see Serum Osmolality)
- Serum Osmolal Gap: variable (depending on the etiology)
Clinical Manifestations
Pharmacologic Manifestations
Enhanced Effect of Neuromuscular Junction Antagonists (see Neuromuscular Junction Antagonists)
- Physiology: acidosis potentiates the effect of neuromuscular junction antagonists
- Agents
- Atracurium (Tracrium) (see Atracurium)
- Cisatracurium (Nimbex) (see Cisatracurium)
- Pancuronium (Pavulon) (see Pancuronium)
- Rocuronium (Zemuron) (see Rocuronium)
- Vecuronium (Norcuron) (see Vecuronium)
Renal Manifestations
- Anion Gap Metabolic Acidosis (AGMA)
Treatment
- Treat Underlying Disorder
References
- The delta gap: an approach to mixed acid-base disorders. Ann Emerg Med. 1990;19:1310–1313 [MEDLINE]
- Management of life-threatening acid-base disorders. First of two parts. N Engl J Med 1998; 338:26-34 [MEDLINE]
- Management of life-threatening acid-base disorders. Second of two parts. N Engl J Med. 1998 Jan 8;338(2):107-11 [MEDLINE]
- Systematic review of current guidelines, and their evidence base, on risk of lactic acidosis after administration of contrast medium for patients receiving metformin. Radiology Jan 2010; 254:261-269
- Treatment of acute metabolic acidosis: a pathophysiologic approach. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2012 Oct;8(10):589-601. doi: 10.1038/nrneph.2012.186. Epub 2012 Sep 4 [MEDLINE]
- Lactic acidosis. N Engl J Med. 2014 Dec 11;371(24):2309-19. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra1309483 [MEDLINE]
- Diagnostic Challenge in a Patient with Severe Anion Gap Metabolic Acidosis. Case Rep Crit Care. 2015;2015:272914. doi: 10.1155/2015/272914. Epub 2015 May 31 [MEDLINE]
