Background
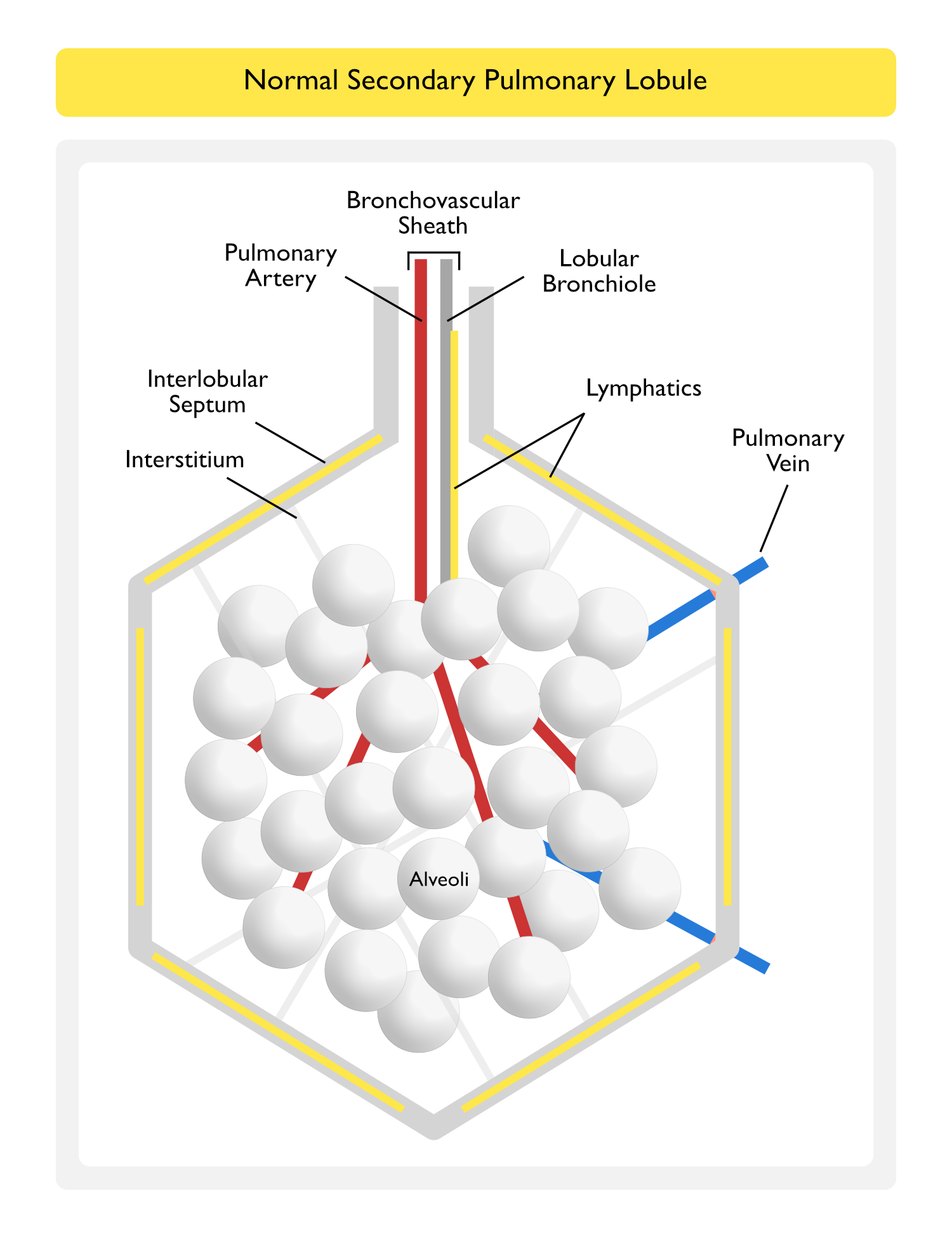
Secondary Pulmonary Lobule (see Pulmonary Anatomy)
The Secondary Pulmonary Lobule is a Functional Unit of the Lung Surrounded by an Interlobular Septum (W.S. Miller [The lung. 2nd ed. Springfield, IL: Charles C Thomas, 1947]) (NEJM, 2020) [MEDLINE]
- The Lobular Bronchiole and a Pulmonary Artery Branch Supply Multiple Acini within a Pulmonary Lobule
- Lymphatics and Pulmonary Veins are Located within the Interlobular Septum
- Lymphatics Also Surround the Bronchovascular Sheath
Etiology of Ground-Glass Infiltrates on the Chest Computed Tomography (Chest CT) Scan (see Chest Computed Tomography)
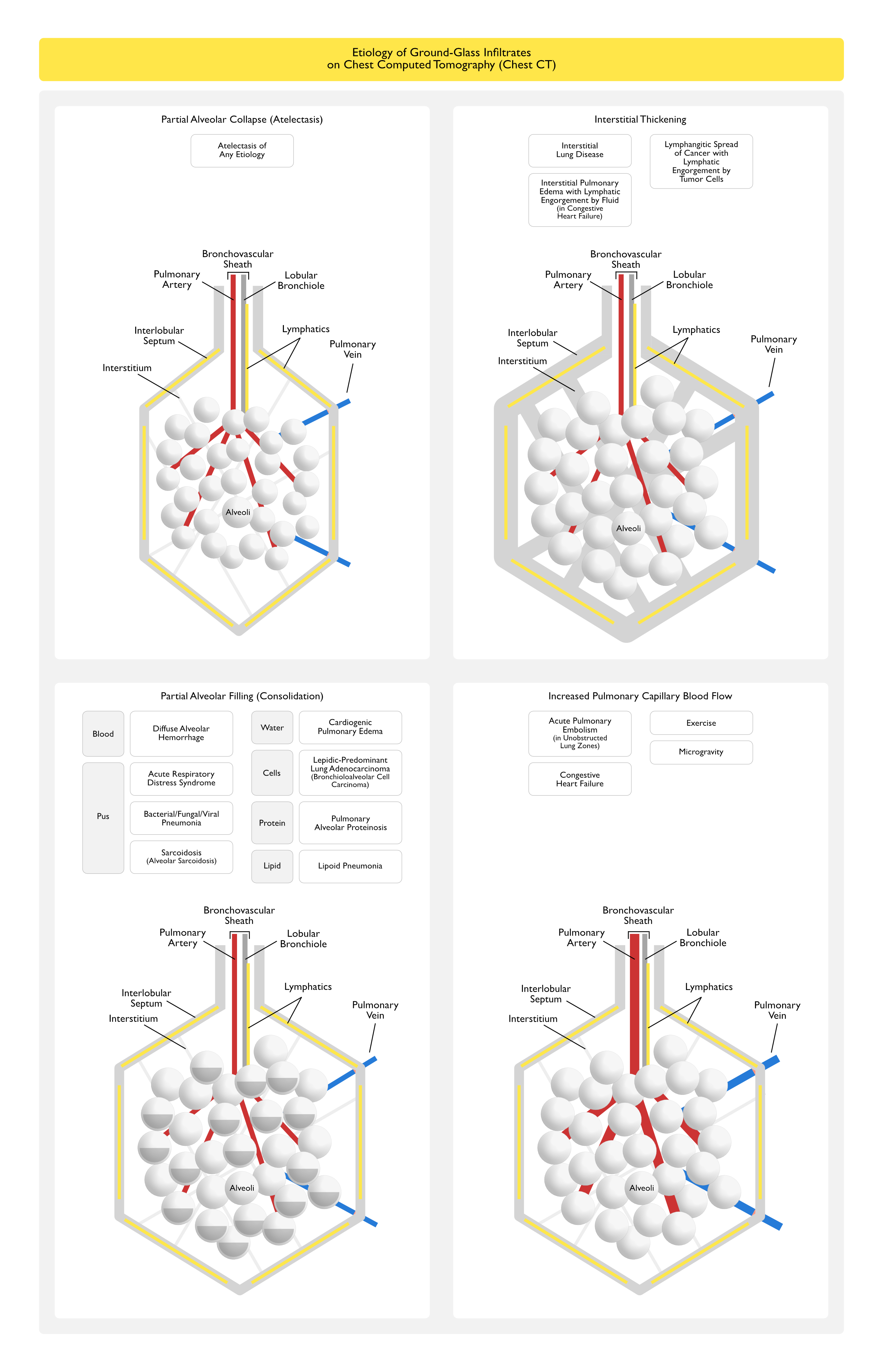
General Comments
- All of the Etiologies of Ground-Glass Infiltrates on the Chest Computed Tomography Below Share the Common Mechanism of Partial Replacement of Lung Air
Ground-Glass Infiltrates Occur on the Chest CT Scan When Air within the Acini in the Pulmonary Lobule is Displaced by Any of the Following Four Mechanisms
Partial Alveolar Collapse (Atelectasis) (see Atelectasis)
- Due to Obstruction, Compression, etc
Interstitial Thickening
- Due to Interstitial Lung Disease (ILD) with Thickening of the Interstitium (see Interstitial Lung Disease)
- Acute Interstitial Pneumonia (AIP) (see Acute Interstitial Pneumonia)
- Cryptogenic Organizing Pneumonia (COP) (see Cryptogenic Organizing Pneumonia)
- Desquamative Interstitial Pneumonia (DIP) (see Desquamative Interstitial Pneumonia)
- Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis (HP) (see Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis)
- Ground-Glass Infiltrates in Respiratory Bronchiolitis-Interstitial Lung Disease Appear Finely Stippled (Due to Presence of Tiny Nodules) (AJR Am J Roentgenol, 2005) [MEDLINE]
- Lymphocytic Interstitial Pneumonia (LIP) (see Lymphocytic Interstitial Pneumonia)
- Nonspecific Interstitial Pneumonia (NSIP) (see Nonspecific Interstitial Pneumonia)
- Respiratory Bronchiolitis-Interstitial Lung Disease (RB-ILD) (see Respiratory Bronchiolitis-Interstitial Lung Disease)
- Ground-Glass Infiltrates in Respiratory Bronchiolitis-Interstitial Lung Disease Appear Finely Stippled (Due to Presence of Tiny Nodules) (AJR Am J Roentgenol, 2005) [MEDLINE]
- Sarcoidosis (see Sarcoidosis)
- Ground-Glass Infiltrates in Sarcoidosis Appear Finely Stippled (Due to Presence of Tiny Nodules) (AJR Am J Roentgenol, 2005) [MEDLINE]
- Due to Interstitial Pulmonary Edema with Lymphatic Engorgement by Fluid (see Pulmonary Edema)
- Cardiogenic Pulmonary Edema Due to Congestive Heart Failure (CHF) (see Cardiogenic Pulmonary Edema and Congestive Heart Failure)
- Due to Lymphangitic Spread of Cancer with Lymphatic Engorgement by Tumor Cells (see Lung Cancer)
- Lung Cancer (see Lung Cancer)
Partial Alveolar Filling (Consolidation)
- Due to Blood
- Diffuse Alveolar Hemorrhage (DAH) (see Diffuse Alveolar Hemorrhage)
- Due to Inflammatory Cells (“Pus”)
- Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) (see Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome)
- Bacterial Pneumonia
- Community-Acquired Pneumonia (CAP) (see Community-Acquired Pneumonia)
- Hospital-Acquired Pneumonia (HAP)/Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia (VAP) (see Hospital-Acquired Pneumonia (HAP) and Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia (VAP))
- Fungal Pneumonia
- Pneumocystis Jirovecii Pneumonia (PJP) (see Pneumocystis Jirovecii)
- Viral Pneumonia
- Cytomegalovirus (CMV) (see Cytomegalovirus)
- Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV) (see Herpes Simplex Virus)
- Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) (see Respiratory Syncytial Virus)
- Sarcoidosis (see Sarcoidosis)
- The Alveolar Sarcoidosis Variant Uniquely Appears as Multiple Large Ground-Glass Masses (AJR Am J Roentgenol, 2005) [MEDLINE]
- Due to Water
- Cardiogenic Pulmonary Edema Due to Congestive Heart Failure (CHF) (see Cardiogenic Pulmonary Edema and Congestive Heart Failure)
- Near Drowning (see Near Drowning)
- Ground-Glass Infiltrates May Be Seen in Some Cases of Near Drowning (J Comput Assist Tomogr, 2000) [MEDLINE]
- Fat Embolism (see Fat Embolism)
- Ground-Glass Infiltrates May Be Seen in Some Cases of Fat Embolism (J Comput Assist Tomogr, 2000) [MEDLINE]
- Due to Malignant Cells
- Lepidic-Predominant Lung Adenocarcinoma (Previously Known as Bronchioloalveolar Cell Carcinoma) (see Lung Cancer) (Radiology, 2001) [MEDLINE] (Ann Thorac Surg, 2002) [MEDLINE] (Proc Am Thorac Soc, 2011) [MEDLINE] (AJR Am J Roentgenol, 2014) [MEDLINE] (Diagn Interv Imaging, 2016) [MEDLINE] (Eur Radiol, 2016) [MEDLINE]
- Due to Proteinaceous Fluid
- Pulmonary Alveolar Proteinosis (see Pulmonary Alveolar Proteinosis)
- Due to Lipid
- Lipoid Pneumonia (see Lipoid Pneumonia)
Increased Pulmonary Capillary Blood Flow/Volume
- Due to Acute Pulmonary Embolism (PE) (see Acute Pulmonary Embolism)
- In Unobstructed Lung Zones, Ground Glass Infiltrates Appeared Immediately After Acute Pulmonary Embolism (Radiology, 2009) [MEDLINE]
- Mechanism
- Redistribution of Blood Flow from Obstructed to Unobstructed Lung Zones, Resulting in Increases in Pressure Artery Pressures (at Levels Consistent with the Development of Pulmonary Edema) (Radiology, 2009) [MEDLINE]
- In Unobstructed Lung Zones, Ground Glass Infiltrates Appeared Immediately After Acute Pulmonary Embolism (Radiology, 2009) [MEDLINE]
- Due to Congestive Heart Failure (CHF) (see Congestive Heart Failure) (Chest, 2004) [MEDLINE]
- Despite the Increase in Pulmonary Capillary Blood Volume, DLCO is Typically Decreased in Congestive Heart Failure
- This is Believed to Be Due to Thickening of the Alveolar-Capillary Barrier from the Accumulation of Fluid or Fibrosis, Resulting in Decreased Alveolar Capillary Membrane Conductance (Chest, 2004) [MEDLINE]
- Despite the Increase in Pulmonary Capillary Blood Volume, DLCO is Typically Decreased in Congestive Heart Failure
- Due to Exercise (J Appl Physiol, 1960) [MEDLINE]
- Due to Microgravity Environment
References
General
- Miller WS. The lung. 2nd ed. Springfield, IL: Charles C Thomas, 1947
- Pulmonary capillary blood volume, flow and diffusing capacity during exercise. J Appl Physiol. 1960 Sep;15:893-902. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1960.15.5.893 [MEDLINE]
- Near drowning: thin-section CT findings in six patients. J Comput Assist Tomogr. Jul-Aug 2000;24(4):562-6. doi: 10.1097/00004728-200007000-00009 [MEDLINE]
- Pulmonary fat embolism syndrome: CT findings in six patients. J Comput Assist Tomogr. Jan-Feb 2000;24(1):24-9. doi: 10.1097/00004728-200001000-00005 [MEDLINE]
- The pulmonary manifestations of left heart failure. Chest. 2004 Feb;125(2):669-82. doi: 10.1378/chest.125.2.669 [MEDLINE]
- Isolated diffuse ground-glass opacity in thoracic CT: causes and clinical presentations. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2005 Feb;184(2):613-22. doi: 10.2214/ajr.184.2.01840613. [MEDLINE]
- Case 25-2020: A 47-Year-Old Woman with a Lung Mass. N Engl J Med. 2020 Aug 13;383(7):665-674. doi: 10.1056/NEJMcpc2004977 [MEDLINE]
Etiology
- CT differentiation of pneumonic-type bronchioloalveolar cell carcinoma and infectious pneumonia. Br J Radiol. 2001;74(882):490-494 [MEDLINE]
- Peripheral lung adenocarcinoma: Correlation of thin-section CT findings with histologic prognostic factors and survival. Radiology 220:803-809, 2001 [MEDLINE]
- “Early” peripheral lung cancer: Prognostic significance of ground glass opacity on thin-section computed tomographic scan. Ann Thorac Surg 74:1635-1639, 2002 [MEDLINE]
- Acute pulmonary embolism: relationships between ground-glass opacification at thin-section CT and hemodynamics in pigs. Radiology. 2009 Mar;250(3):721-9. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2503081134 [MEDLINE]
- International association for the study of lung cancer/american thoracic society/european respiratory society international multidisciplinary classification of lung adenocarcinoma. J Thorac Oncol. 2011 Feb;6(2):244-85. doi: 10.1097/JTO.0b013e318206a221 [MEDLINE]
- Pure ground-glass opacity neoplastic lung nodules: Histopathology, imaging, and management. AJR Am J Roentgenol 202:W224-W233, 2014 [MEDLINE]
- Lung adenocarcinomas: Correlation of computed tomography and pathology findings. Diagn Interv Imaging 97:955-963, 2016 [MEDLINE]
- Software performance in segmenting ground-glass and solid components of subsolid nodules in pulmonary adenocarcinomas. Eur Radiol 26:4465-4474, 2016 [MEDLINE]
