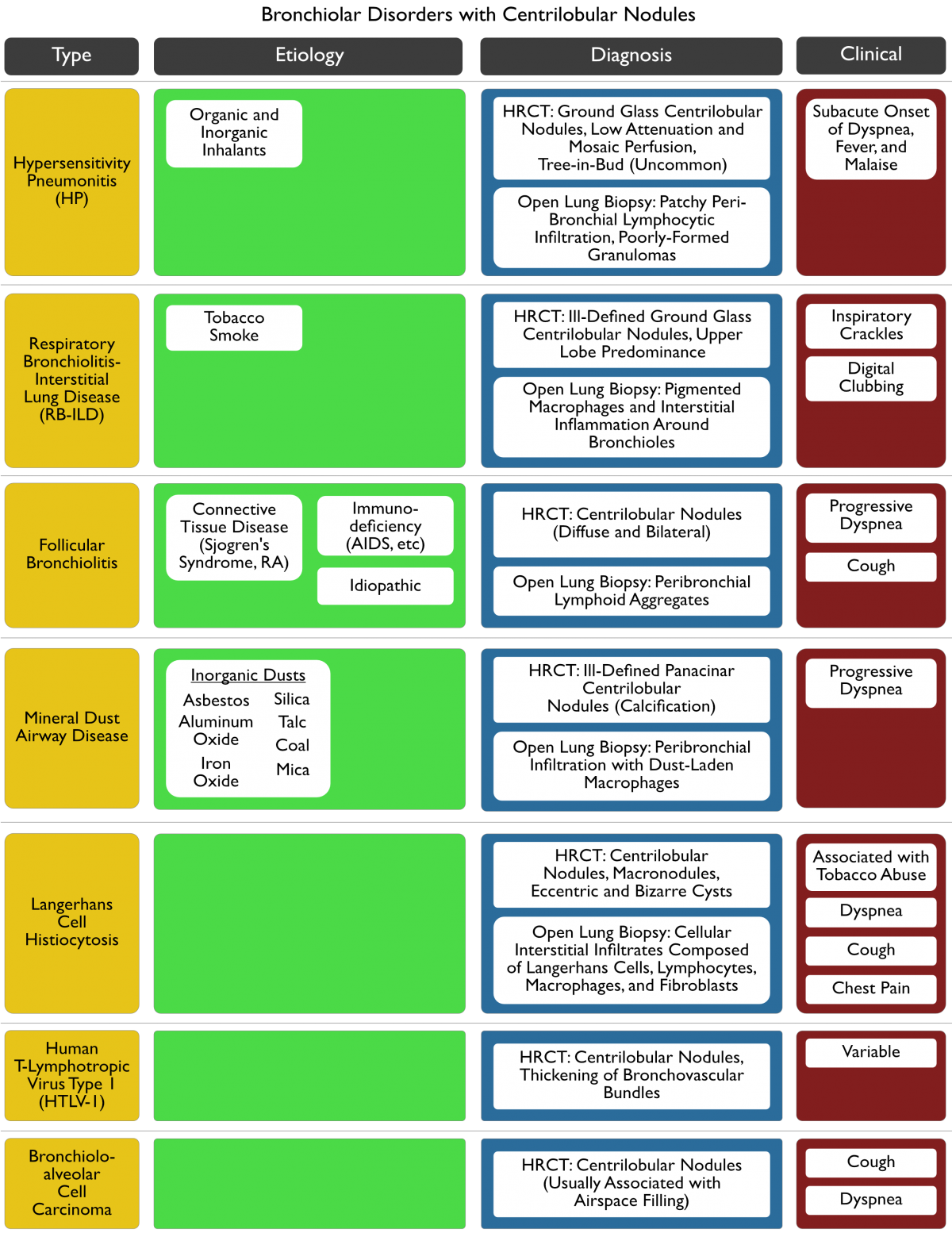
Etiology
Infection
Viral
- Cytomegalovirus (CMV) (see Cytomegalovirus, [[Cytomegalovirus]])
- Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) (see Epstein-Barr Virus, [[Epstein-Barr Virus]])
- Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) (see Human Immunodeficiency Virus, [[Human Immunodeficiency Virus]])
- Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV) (see Herpes Simplex Virus, [[Herpes Simplex Virus]])
- Influenza Virus (see Influenza Virus, [[Influenza Virus]])
- Measles Virus (see Measles Virus, [[Measles Virus]])
- Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) (see Respiratory Syncytial Virus, [[Respiratory Syncytial Virus]])
- Varicella-Zoster Virus (VZV) (see Varicella-Zoster Virus, [[Varicella-Zoster Virus]])
Bacterial
- Aspiration Pneumonia (see Aspiration Pneumonia, [[Aspiration Pneumonia]])
- Chlamydia Trachomatis (see Chlamydia Trachomatis, [[Chlamydia Trachomatis]])
- Legionellosis (see Legionellosis, [[Legionellosis]])
- Patchy Lobar Infiltrate, Which Progresses to Consolidation: most common pattern
- Diffuse Interstitial Infiltrates: this pattern has also been reported
- Miliary Tuberculosis (Disseminated Tuberculosis) (see Tuberculosis, [[Tuberculosis]])
- Mycobacterium Kansasii (see Mycobacterium Kansasii, [[Mycobacterium Kansasii]])
- Nocardiosis (see Nocardiosis, [[Nocardiosis]])
- Post-Infectious Interstitial Lung Disease
- Salmonella (see Salmonella, [[Salmonella]])
- Staphylococcus Aureus (see Staphylococcus Aureus, [[Staphylococcus Aureus]])
Fungal
- Coccidioidomycosis (see Coccidioidomycosis, [[Coccidioidomycosis]])
- Cryptococcosis (see Cryptococcosis, [[Cryptococcosis]])
- Pneumocystis Jirovecii (see Pneumocystis Jirovecii, [[Pneumocystis Jirovecii]])
Parasitic
- Cryptosporidiosis (see Cryptosporidiosis, [[Cryptosporidiosis]])
- Toxoplasmosis (see Toxoplasmosis, [[Toxoplasmosis]])
Neoplasm
- Angioimmunoblastic Lymphadenopathy (see Angioimmunoblastic Lymphadenopathy, [[Angioimmunoblastic Lymphadenopathy]])
- Bronchioloalveolar Cell Carcinoma (see Bronchioloalveolar Cell Carcinoma, [[Bronchioloalveolar Cell Carcinoma]])
- Lung Metastases-Lymphangitic Carcinomatosis (see Lung Metastases-Lymphangitic Carcinomatosis, [[Lung Metastases-Lymphangitic Carcinomatosis]])
- Lung Metastases-Miliary (see Lung Metastases-Miliary, [[Lung Metastases-Miliary]])
- Multiple Myeloma (see Multiple Myeloma, [[Multiple Myeloma]])
- Primary Pulmonary Hodgkins Disease (see Primary Pulmonary Hodgkins Disease, [[Primary Pulmonary Hodgkins Disease]])
- Primary Pulmonary Lymphoma (see Primary Pulmonary Lymphoma, [[Primary Pulmonary Lymphoma]])
Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis (HP) (see Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis, [[Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis]])
- Vegetable Products
- Animal Products
- Insect products
- Reactive Simple Chemicals
- Drugs
Pneumoconiosis
- Aluminum Dust Pneumoconiosis (see Aluminum, [[Aluminum]])
- Asbestosis (see Asbestos, [[Asbestos]])
- Berylliosis (see Beryllium, [[Beryllium]])
- Coal Worker’s Pneumoconiosis (see Coal Workers Pneumoconiosis, [[Coal Workers Pneumoconiosis]])
- Cobalt Pneumoconiosis (see Cobalt, [[Cobalt]]): combination of tungsten carbide + cobalt -> known as Hard Metal Pneumoconiosis
- Nylon Flock Worker’s Lung (see Nylon Flock Workers Lung, [[Nylon Flock Workers Lung]])
- Siderosis (see Siderosis, [[Siderosis]])
- Silicosis (see Silicosis, [[Silicosis]])
- Stannosis (see Stannosis, [[Stannosis]])
- Talc Pneumoconiosis (see Talc, [[Talc]])
- Titanium (see Titanium, [[Titanium]])
Rheumatologic, Connective Tissue, and Autoimmune Disease
- Adult-Onset Still’s Disease (see Adult-Onset Still’s Disease, [[Adult-Onset Stills Disease]])
- Ankylosing Spondylitis (see Ankylosing Spondylitis, [[Ankylosing Spondylitis]])
- Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia (see Hemolytic Anemia, [[Hemolytic Anemia]])
- Immune Thrombocytopenic Purpura (see Immune Thrombocytopenic Purpura, [[Immune Thrombocytopenic Purpura]])
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease (see Inflammatory Bowel Disease, [[Inflammatory Bowel Disease]])
- Mixed Connective Tissue Disease (MCTD) (see Mixed Connective Tissue Disease, [[Mixed Connective Tissue Disease]])
- Mixed Cryoglobulinemia (see Cryoglobulinemia, [[Cryoglobulinemia]])
- Polydermatomyositis (see Polydermatomyositis, [[Polydermatomyositis]])
- Primary Biliary Cirrhosis (PBC) (see Primary Biliary Cirrhosis, [[Primary Biliary Cirrhosis]])
- Psoriasis (see Psoriasis, [[Psoriasis]])
- Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) (see Rheumatoid Arthritis, [[Rheumatoid Arthritis]])
- Scleroderma (see Scleroderma, [[Scleroderma]])
- Sjogrens Syndrome (see Sjogrens Syndrome, [[Sjogrens Syndrome]])
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) (see Systemic Lupus Erythematosus, [[Systemic Lupus Erythematosus]])
- Temporal Arteritis (see Temporal Arteritis, [[Temporal Arteritis]])
Pulmonary Infiltrates with Eosinophilia (see Pulmonary Infiltrates with Eosinophilia, [[Pulmonary Infiltrates with Eosinophilia]])
- Acute Lung Transplant Rejection (Acute Cellular Lung Transplant Rejection) (see Acute Lung Transplant Rejection, [[Acute Lung Transplant Rejection]]): peripheral eosinophilia may occur with/without pulmonary infiltrates (as acute rejection may be detected by surveillance bronchoscopy with transbronchial biopsy prior to the development of pulmonary infiltrates)
- Chronic Eosinophilic Pneumonia (see Chronic Eosinophilic Pneumonia, [[Chronic Eosinophilic Pneumonia]])
- Eosinophilia-Myalgia Syndrome (see Eosinophilia-Myalgia Syndrome, [[Eosinophilia-Myalgia Syndrome]])
- Sarcoidosis (see Sarcoidosis, [[Sarcoidosis]])
- Tropical Pulmonary Eosinophilia (Occult Filariasis) (see Tropical Pulmonary Eosinophilia, [[Tropical Pulmonary Eosinophilia (Occult Filariasis)]])
Unclassified Interstitial Lung Disease
- Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) (see Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome, [[Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome]])
- Amyloidosis (see Amyloidosis, [[Amyloidosis]])
- Bronchiolitis Obliterans (BO) (see Bronchiolitis Obliterans, [[Bronchiolitis Obliterans]])
- Chronic Aspiration Pneumonia (see Aspiration Pneumonia, [[Aspiration Pneumonia]])
- Chronic Pulmonary Edema (see Pulmonary Edema, [[Pulmonary Edema]])
- Chronic Uremia
- Combined Pulmonary Fibrosis and Emphysema (see Combined Pulmonary Fibrosis and Emphysema, [[Combined Pulmonary Fibrosis and Emphysema]])
- Dyskeratosis Congenita (see Dyskeratosis Congenita, [[Dyskeratosis Congenita]])
- Follicular Bronchiolitis (see Follicular Bronchiolitis, [[Follicular Bronchiolitis]])
- Gaucher’s Disease (see Gauchers Disease, [[Gauchers Disease]])
- Hermansky-Pudlak Syndrome (see Hermansky-Pudlak Syndrome, [[Hermansky-Pudlak Syndrome]])
- Hypocalciuric Hypercalcemia Syndrome (see Hypocalciuric Hypercalcemia Syndrome, [[Hypocalciuric Hypercalcemia Syndrome]])
- Interstitial Pulmonary Edema (see Pulmonary Edema, [[Pulmonary Edema]])
- Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis (LCH) (see Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis, [[Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis]])
- Lipoid Pneumonia (see Lipoid Pneumonia, [[Lipoid Pneumonia]])
- Lymphangioleiomyomatosis (LAM) (see Lymphangioleiomyomatosis, [[Lymphangioleiomyomatosis]])
- Metastatic Calcification (see Metastatic Calcification, [[Metastatic Calcification]])
- Niemann-Pick Disease (see Niemann-Pick Disease, [[Niemann-Pick Disease]])
- Neurofibromatosis (see Neurofibromatosis, [[Neurofibromatosis]])
- Pulmonary Alveolar Microlithiasis (see Pulmonary Alveolar Microlithiasis, [[Pulmonary Alveolar Microlithiasis]])
- Pulmonary Alveolar Proteinosis (see Pulmonary Alveolar Proteinosis, [[Pulmonary Alveolar Proteinosis]])
- Radiation Pneumonitis and Fibrosis (see Radiation Pneumonitis and Fibrosis, [[Radiation Pneumonitis and Fibrosis]])
- Recurrent Diffuse Alveolar Hemorrhage (see Diffuse Alveolar Hemorrhage, [[Diffuse Alveolar Hemorrhage]])
- Microscopic Polyangiitis (see Microscopic Polyangiitis, [[Microscopic Polyangiitis]])
- Mitral Stenosis (see Mitral Stenosis, [[Mitral Stenosis]])
- Wegener’s Granulomatosis (see Wegeners Granulomatosis, [[Wegeners Granulomatosis]])
- Sickle Cell Disease (see Sickle Cell Disease, [[Sickle Cell Disease]])
- Tuberous Sclerosis (see Tuberous Sclerosis, [[Tuberous Sclerosis]])
Drug/Toxin
- Alkylating Agents
- Nitrogen Mustards
- Chlorambucil (see Chlorambucil, [[Chlorambucil]])
- Cyclophosphamide (Cytoxan) (see Cyclophosphamide, [[Cyclophosphamide]])
- Ifosfamide (see Ifosfamide, [[Ifosfamide]])
- Melphalan (see Melphalan, [[Melphalan]])
- Nitrosoureas (see Nitrosoureas, [[Nitrosoureas]])
- Carmustine (BCNU) (see Carmustine, [[Carmustine]]): unusually, interstitial lung disease can occur wks-yrs after discontinuation
- Chlorozotocin (see Chlorozotocin, [[Chlorozotocin]])
- Fotemustine (see Fotemustine, [[Fotemustine]])
- Lomustine (CCNU) (see Lomustine, [[Lomustine]])
- Semustine (methyl-CCNU) (see Semustine, [[Semustine]])
- Alkyl Sulfonates
- Busulfan (see Busulfan, [[Busulfan]])
- Nitrogen Mustards
- All-Trans Retinoic Acid (ATRA) (see All-Trans Retinoic Acid, [[All-Trans Retinoic Acid]])
- Amiodarone (Cordarone) (see Amiodarone, [[Amiodarone]])
- Anti-Tumor Necrosis Factor-α (Anti-TNFα) Therapy (see Anti-Tumor Necrosis Factor-α Therapy, [[Anti-Tumor Necrosis Factor-α Therapy]])
- Adalimumab (Humira) (see Adalimumab, [[Adalimumab]])
- Etanercept (Enbrel) (see Etanercept, [[Etanercept]])
- Infliximab (Remicade) (see Infliximab, [[Infliximab]])
- Azacitidine (Vidaza) (see Azacitidine, [[Azacitidine]])
- Epidemiology: case reports
- Azathioprine (Imuran) (see Azathioprine, [[Azathioprine]])
- Bacillus Calmette-Guerin (BCG) (see Bacillus Calmette-Guerin, [[Bacillus Calmette-Guerin]])
- Beta Blockers (see β-Adrenergic Receptor Antagonists, [[β-Adrenergic Receptor Antagonists]])
- Acebutolol (Sectral, Prent) (see Acebutolol, [[Acebutolol]])
- Atenolol (Tenormin) (see Atenolol, [[Atenolol]])
- Carvedilol (Coreg) (see Carvedilol, [[Carvedilol]])
- Celiprolol
- Labetalol (see Labetalol, [[Labetalol]])
- Nadolol (see Nadolol, [[Nadolol]])
- Pindolol (see Pindolol, [[Pindolol]])
- Practolol (see Practolol, [[Practolol]])
- Propafenone (Rhythmol) (see Propafenone, [[Propafenone]])
- Propanolol (see Propanolol, [[Propanolol]])
- Timolol (see Timolol, [[Timolol]])
- Bleomycin (see Bleomycin, [[Bleomycin]])
- Bromocriptine (Parlodel, Cycloset, Brotin) (see Bromocriptine, [[Bromocriptine]])
- Cetuximab (Erbitux) (see Cetuximab, [[Cetuximab]])
- Cocaine (see Cocaine, [[Cocaine]])
- Dronedarone (Multaq) (see Dronedarone, [[Dronedarone]])
- Erlotinib (Tarceva) (see Erlotinib, [[Erlotinib]])
- Etoposide (VP-16) (see Etoposide, [[Etoposide]])
- Everolimus (see Everolimus, [[Everolimus]])
- Flecainide (see Flecainide, [[Flecainide]])
- Fludarabine (Fludara) (see Fludarabine, [[Fludarabine]])
- Gefitinib (Iressa) (see Gefitinib, [[Gefitinib]])
- Gold (see Gold, [[Gold]])
- Heroin (see Heroin, [[Heroin]])
- Hydralazine (see Hydralazine, [[Hydralazine]]): drug-induced SLE (see Systemic Lupus Erythematosus, [[Systemic Lupus Erythematosus]])
- Hydrochlorothiazide (HCTZ) (see Hydrochlorothiazide, [[Hydrochlorothiazide]])
- Hydroxyurea (Hydroxycarbamide, Hydrea, Droxia) (see Hydroxyurea, [[Hydroxyurea]])
- Imatinib (Gleevec) (see Imatinib, [[Imatinib]])
- Interferons (see Interferons, [[Interferons]])
- Irinotecan (Camptosar) (see Irinotecan, [[Irinotecan]])
- Isoniazid (INH) (see Isoniazid, [[Isoniazid]]): drug-induced SLE (see Systemic Lupus Erythematosus, [[Systemic Lupus Erythematosus]])
- Leflunomide (see Leflunomide, [[Leflunomide]])
- Lenalidomide (Revlimid) (see Lenalidomide, [[Lenalidomide]])
- L-Tryptophan (see Eosinophilia-Myalgia Syndrome, [[Eosinophilia-Myalgia Syndrome]])
- Mercaptopurine (see Mercaptopurine, [[Mercaptopurine]])
- Mesalamine (5-ASA, 5-Aminosalicylic Acid) (see Mesalamine, [[Mesalamine]])
- Methadone (see Methadone, [[Methadone]])
- Methotrexate (see Methotrexate, [[Methotrexate]])
- Mitomycin C (see Mitomycin, [[Mitomycin]])
- Mechanistic Target of Rapamycin (mTOR) Inhibitors (see Mechanistic Target of Rapamycin Inhibitors, [[Mechanistic Target of Rapamycin Inhibitors]])
- Sirolimus (Rapamune, Rapamycin) (see Sirolimus, [[Sirolimus]])
- Temsirolimus (see Temsirolimus, [[Temsirolimus]])
- Nilutemide
- Nitrofurantoin (Macrodantin) (see Nitrofurantoin, [[Nitrofurantoin]])
- Oxaliplatin (Eloxatin, Oxaliplatin Medac) (see Oxaliplatin, [[Oxaliplatin]])
- Oxygen Toxicity (see Oxygen, [[Oxygen]])
- Paraquat Intoxication (see Paraquat, [[Paraquat]])
- PD-1 Checkpoint Inhibitors
- Nivolumab (Opdivo) (see Nivolumab, [[Nivolumab]])
- Pembrolizumab (Keytruda) (see Pembrolizumab, [[Pembrolizumab]])
- Penicillamine (see Penicillamine, [[Penicillamine]])
- Phenytoin (Dilantin) (see Phenytoin, [[Phenytoin]]): drug-induced SLE (see Systemic Lupus Erythematosus, [[Systemic Lupus Erythematosus]])
- Piritrexim (see Piritrexim, [[Piritrexim]])
- Pomalidomide (Pomalyst) (see Pomalidomide, [[Pomalidomide]])
- Procainamide (see Procainamide, [[Procainamide]]): drug-induced SLE (see Systemic Lupus Erythematosus, [[Systemic Lupus Erythematosus]])
- Procarbazine (see Procarbazine, [[Procarbazine]])
- Propoxyphene (Darvon) (see Propoxyphene, [[Propoxyphene]])
- Pyrimidine Analogues
- Cytarabine (ARA-C, Cytosar-U) (see Cytarabine, [[Cytarabine]])
- Gemcitabine (Gemzar) (see Gemcitabine, [[Gemcitabine]])
- Rituximab (Rituxan) (see Anti-CD20 Therapy, [[Anti-CD20 Therapy]])
- Sorafenib (Nexavar) (see Sorafenib, [[Sorafenib]]): uncommon (occurs in 0.1-1% of cases)
- Sulfapyridine (see Sulfonamides, [[Sulfonamides]])
- Sulfasalazine (Azulfidine) (see Sulfasalazine, [[Sulfasalazine]])
- Sulfur Mustard Gas Inhalation (see Sulfur Mustard Gas, [[Sulfur Mustard Gas]])
- Talc Granulomatosis (see Talc Granulomatosis, [[Talc Granulomatosis]])
- Taxanes (see Taxanes, [[Taxanes]])
- Docetaxel (Taxotere) (see Docetaxel, [[Docetaxel]])
- Paclitaxel (Taxol) (see Paclitaxel, [[Paclitaxel]])
- Temozolomide (Temodar, Temodal) (see Temozolomide, [[Temozolomide]])
- Tocainide (see Tocainide, [[Tocainide]])
- Trastuzumab (Herceptin) (see Trastuzumab, [[Trastuzumab]])
- Vinblastine (see Vinblastine, [[Vinblastine]])
- Zinostatin (see Zinostatin, [[Zinostatin]])
Diagnosis
Complete Blood Count (CBC) (see Complete Blood Count, [[Complete Blood Count]])
- Leukopenia (see Leukopenia, [[Leukopenia]])
- Sarcoidosis (see Sarcoidosis, [[Sarcoidosis]])
- Connective Tissue Disease
- Lymphoma
- Drug-induced ILD
- Leukocytosis (see xxxx, [[xxxx]])
- Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis (HP) (see Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis, [[Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis]])
- Lymphoma
- Drug-induced ILD
- Systemic Vasculitis
- Eosinophilia (see Peripheral Eosinophilia, [[Peripheral Eosinophilia]])
- Pulmonary Infiltrates with Eosinophilia (PIE) (see xxxx, [[xxxx]])
- Thrombocytopenia (see Thrombocytopenia, [[Thrombocytopenia]])
- Sarcoidosis (see Sarcoidosis, [[Sarcoidosis]])
- Connective Tissue Disease
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) (see Systemic Lupus Erythematosus, [[Systemic Lupus Erythematosus]])
- Drug-induced Interstitial Lung Disease
- Gaucher’s Disease
- Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF)
- Normocytic Anemia (see Anemia, [[Anemia]])
- Diffuse Alveolar Hemorrhage
- Connective Tissue Disease
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) (see Systemic Lupus Erythematosus, [[Systemic Lupus Erythematosus]])
- Pulmonary Metastases-Lymphangitic Carcinomatosis
- Hemolytic Anemia (see Hemolytic Anemia, [[Hemolytic Anemia]])
- Sarcoidosis (see Sarcoidosis, [[Sarcoidosis]])
- Connective Tissue Disease
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) (see Systemic Lupus Erythematosus, [[Systemic Lupus Erythematosus]])
- Lymphoma
- Drug-Induced Interstitial Lung Disease
- Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF) (see xxxx, [[xxxx]])
Urinalysis (see Urinalysis, [[Urinalysis]])
- Abnormal Urinary Sediment
- Connective tissue disease
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) (see Systemic Lupus Erythematosus, [[Systemic Lupus Erythematosus]])
- Systemic Vasculitis
- Drug-Induced Interstitial Lung Disease
- Connective tissue disease
Immunoglobulin Levels
- Hypogammaglobulinemia
- Lymphocytic Interstitial Pneumonia (LIP) (see xxxx, [[xxxx]])
- Hypergammaglobulinemia
- *Lymphocytic Interstitial Pneumonia]]
- Connective Tissue Disease
- Systemic Vasculitis
- Sarcoidosis (see Sarcoidosis, [[Sarcoidosis]])
- Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis]
- Asbestosis
- Silicosis
- Lymphoma
Serum Angiotensin Converting Enzyme (ACE) Level (see Serum Angiotensin Converting Enzyme, [[Serum Angiotensin Converting Enzyme]])
- Elevated Angiotensin Converting Enzyme (ACE) Level
- Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) (see Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome, [[Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome]])
- Gaucher’s Disease (see xxxx, [[xxxx]])
- Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis (HP) (see Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis, [[Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis]])
- Sarcoidosis
- Silicosis
Pulmonary Function Tests (PFT’s) (see Pulmonary Function Tests, [[Pulmonary Function Tests]])
- Obstruction
- Sarcoidosis (see Sarcoidosis, [[Sarcoidosis]])
- Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis (see Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis, [[Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis]])
- Lymphangioleiomyomatosis (LAM) (see Lymphangioleiomyomatosis, [[Lymphangioleiomyomatosis]])
- Sjogrens Syndrome with Follicular Bronchiolitis (see Follicular Bronchiolitis, [[Follicular Bronchiolitis]])
- Tuberous Sclerosis (see Tuberous Sclerosis, [[Tuberous Sclerosis]])
General Radiographic Features
Normal Chest X-Ray (CXR) (see Chest X-Ray, [[Chest X-Ray]])
- General Comments: normal CXR is seen in 10% of all ILD cases, but these usually have abnormal HRCT
- Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis (HP) (see Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis, [[Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis]]): may be normal in some cases discovered in population studies, rarely normal in isolated chronic HP cases
- Sarcoidosis (see Sarcoidosis, [[Sarcoidosis]])
- Bronchiolitis Obliterans (BO) (see xxxx, [[xxxx]])
- Connective Tissue Disease
- Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF): early in course
- Asbestosis
- Lymphangioleiomyomatosis (LAM) (see Lymphangioleiomyomatosis, [[Lymphangioleiomyomatosis]])
Upper Lung Zone-Predominance
- Amiodarone (see xxxx, [[xxxx]])
- Berylliosis
- Carmustine (see xxxx, [[xxxx]])
- Chronic Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis (HP) (see Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis, [[Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis]])
- Gold (see xxxx, [[xxxx]])
- Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis (see Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis, [[Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis]])
- Neurofibromatosis
- Nodular Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) (see xxxx, [[xxxx]])
- Radiation Pneumonitis (see Radiation Pneumonitis and Fibrosis, [[Radiation Pneumonitis and Fibrosis]])
- Sarcoidosis (see Sarcoidosis, [[Sarcoidosis]])
- Silicosis (see xxxx, [[xxxx]])
Alveolar Filling Pattern
- [[Bronchioloalveolar Cell Carcinoma]]: alveoli filled with malignant cells and mucinous material
- [[Diffuse Alveolar Hemorrhage]]: alveoli filled with blood or hemosiderin-laden macrophages
- [[Acute Eosinophilic Pneumonia]]:
- [[Chronic Eosinophilic Pneumonia]]
- [[Cryptogenic Organizing Pneumonia]]
- [[Pulmonary Alveolar Proteinosis]]: alveoli filled with proteinaceous material
- [[Lymphoma]]: alveoli filled with malignant lymphocytes
- [[Lymphocytic Interstitial Pneumonia]]: alveoli filled with lymphoplasmacytic cells
- [[Sarcoidosis]]: alveoli filled with granulomas or lymphycte-macrophage alveolitis
- [[Desquamative Interstitial Pneumonia]]: alveoli filled with macrophages
- [[Pulmonary Infiltrates with Eosinophilia]]: alveoli filled with eosinophils, macrophages, and lymphocytes
- [[Pulmonary Alveolar Microlithiasis]]: alveoli filled with calcium-phosphate microliths
- [[Cryptogenic Organizing Pneumonia]]: alveoli filled with collagen
- [[Lipoid Pneumonia]]: alveoli filled with lipid-filled macrophages
- [[Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis]]: alveoli filled with lymphoplasmacytic cells
Preserved or Increased Lung Volumes
- Respiratory Bronchiolitis Interstitial Lung Disease
- Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis (see Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis, [[Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis]])
- Lymphangioleiomyomatosis (LAM) (see Lymphangioleiomyomatosis, [[Lymphangioleiomyomatosis]])
- Tuberous Sclerosis
- Sarcoidosis
- Neurofibromatosis
- Chronic Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis
Honeycombing
- [[Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis]]
- Connective Tissue Disease-Associated ILD
- [[Asbestosis]]
- Drug-Induced ILD
- [[Lymphocytic Interstitial Pneumonia]]
- Chronic [[Aspiration Pneumonia]]
- [[Idiopathic Pulmonary Hemosiderosis]]
- [[Hermansky-Pudlak Syndrome]]
- [[Pulmonary Alveolar Proteinosis]]
Pneumothorax
- Lymphangioleiomyomatosis (LAM) (see Lymphangioleiomyomatosis, [[Lymphangioleiomyomatosis]])
- Tuberous Sclerosis (see Tuberous Sclerosis, [[Tuberous Sclerosis]])
- Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis (see Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis, [[Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis]])
- Neurofibromatosis
- Bullous-Cystic Sarcoidosis (see Sarcoidosis, [[Sarcoidosis]])
Pleural Involvement
- [[Lung Metastases-Lymphangitic Carcinomatosis]]: pleural effusion
- Connective Tissue Disease-Associated ILD ([[SLE]], [[Rheumatoid Arthritis]]): pleural effusion
- [[Nitrofurantoin]]: pleural effusion
- [[Sarcoidosis]]: pleural effusion
- Radiation Pneumonitis (see [[Radiation Pneumonitis and Fibrosis]]): pleural effusion
- [[Lymphangioleiomyomatosis]]: chylothorax
- [[Asbestosis]]: pleural calcifications
Hilar/Mediastinal Adenopathy
- Sarcoidosis (see Sarcoidosis, [[Sarcoidosis]])
- [[Lymphoma]]
- [[Lung Metastases-Lymphangitic Carcinomatosis]]
- [[Lymphocytic Interstitial Pneumonia]]
- [[Berylliosis]]
- [[Amyloidosis]]
- [Gauchers Disease]]
Eggshell Calcification of Lymph Nodes
- Silicosis (see xxxx, [[xxxx]])
- Sarcoidosis (see Sarcoidosis, [[Sarcoidosis]])
- Radiation Fibrosis (see Radiation Pneumonitis and Fibrosis, [[Radiation Pneumonitis and Fibrosis]])
Kerley B Lines
- Lung Metastases-Lymphangitic Carcinomatosis
- Lymphangioleiomyomatosis
- Pulmonary Venous Hypertension
- Mitral Stenosis
- Pulmonary Veno-Occlusive Disease
- Lymphoma
- Amyloidosis
High-Resolution Chest CT (HRCT) (see High-Resolution Chest Computed Tomography, [[High-Resolution Chest Computed Tomography]])
High-Resolution Chest CT Patterns
- Normal HRCT
- Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis (HP) (see Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis, [[Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis]])
- Interlobular Septal Thickening
- Lymphangitic Spread
- Crazy Paving Pattern: fine reticular pattern superimposed on ground glass opacification, due to thickening of intralobular interstitium -> creates geometric shapes) -> this pattern is fairly non-specific
- PAP: classic association
- UIP
- Infection: PCP
- Pulmonary edema
- ARDS
- BOOP
- DAH
- XRT
- SARS
- Bronchoalveolar Carcinoma
- Sarcoidosis
- Lipoid Pneumonia
- Ground Glass
- Mycoplasma: central pattern of ground-glass opacification and consolidation
- Chlamydia: central pattern of ground-glass opacification and consolidation
- Influenza: central pattern of ground-glass opacification and consolidation
- SARS: peripheral, lower-lobe predominance
- PCP: central ground-glass or mosaic pattern
- AIP:
- RB-ILD/DIP
- NSIP
- UIP/IPF
- COP/BOOP
- LIP
- Centrilobular Nodules with Peripheral Tree-In-Bud: indicates bronchiolar disease
High-Resolution Chest CT Patterns by Disease (see High-Resolution Chest Computed Tomography, [[High-Resolution Chest Computed Tomography]])
- HRCT in Mycoplasma/Chlamydia/Influenza: central pattern of ground-glass (due to airspace filling) and consolidation: may progress to centrilobular, acinar shadows and air-space consolidation with a lobular distribution
- High-Resolution Chest CT in Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis (see xxxx, [[xxxx]])
- Location of Infiltrates: predominantly in the middle lung zone, sparing the lower lobes
- Ground-glass (due to airspace filling) with consolidation:
- Alveolar inflammation:
- Centrilobular nodules (due to bronchiolocentric distribution of disease): may be present
- High-Resolution Chest CT in Chronic Eosinophilic Pneumonia (see xxxx, [[xxxx]])
- Location of Infiltrates: predominantly in middle and upper lobes
- Ground glass (due to airspace filling) with/without consolidation: consolidation present in 74% of cases
- High-Resolution Chest CT in Cryptogenic Organizing Pneumonia (see xxxx, [[xxxx]])
- Location of Infiltrates: predominantly in periphery, lower lobes
- Ground glass (due to airspace filling) with/without consolidation: consolidation (usually patchy) present in 87% of cases
- “Crazy Paving” Pattern: ground-glass with thickening of interlobular and intralobular septa, producing polygonal shapes
- Bronchiectasis: may be seen
- Nodules (32% of cases)”
- Lymphadenopathy (13% of cases):
- Pleural effusion (20% of cases):
- High-Resolution Chest CT in SARS
- Location of Infiltrates: predominantly in periphery, lower lobes (appears similar to [[Cryptogenic Organizing Pneumonia]])
- Ground glass (due to airspace filling) with/without consolidation: common feature
- “Crazy Paving” Pattern: ground-glass with thickening of interlobular and intralobular septa, producing polygonal shapes
- Bronchiectasis: may be seen
- High-Resolution Chest CT in PAP
- “Crazy Paving” Pattern: ground-glass with thickening of interlobular and intralobular septa, producing polygonal shapes
- Predominantly central alveolar opacities in mid-lower lung zones, sparing subpleural areas and areas adjacent to diaphragm and heart
- Mosaic Pattern:
- High-Resolution Chest CT in Acute Interstitial Pneumonia (AIP)
- Patchy or Diffuse Ground Glass Infiltrates (Due to Airspace Filling)
- High-Resolution Chest CT in DIP
- Ground glass (Due to Airspace Filling) without Polygonal Lines
- High-Resolution Chest CT in Lymphangitic Mets
- Diffuse reticulonodular infiltrates, often with linear markings radiating out from enlarged hilar or mediastinal nodes
- “Beaded chain” or “string of pearls” thickening of interlobular septa (mainly at periphery of lung and extending to the pleural surface) due to pulmonary lymphatic obstruction -> producing polygonal shapes
- Intevervening parenchyma between the interlobular septa is typically normal (unlike in IPF, where it is usually distorted or honeycombed)
- Presence of lymphangitic pattern in patient with known malignancy: 70-80% probability of metastases being etiologic
- High-Resolution Chest CT in Interstitial Pulm Edema
- Smoothly thickened interlobular septa -> producing polygonal shapes
- High-Resolution Chest CT in Diffuse Alveolar Hemorhage (DAH)
- Ground glass (due to airspace filling)
Bronchoscopy (see Bronchoscopy, [[Bronchoscopy]])
Bronchoalveolar Lavage (BAL)
Recommendations for Bronchoalveolar Lavage (BAL) in the Setting of Interstitial Lung Disease (Am J Respir Crit Care Med, 2012) [MEDLINE]
- For Patients with Suspected Interstitial Lung Disease in Whom a Bronchoalveolar Lavage Can Be Tolerated, BAL Target Site Be Chosen on the Basis of an HRCT Performed Before the Procedure, Rather than Choosing a Traditional Bronchoalveolar Lavage Site (Such as the Right Middle Lobe or Lingula)
- HRCT Should Be Performed within 6 wks of the BAL
- For Patients with Suspected Interstitial Lung Disease Who Undergo Bronchoalveolar Lavage, a Differential Cell Count Should Be Performed on the Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid
- Including Lymphocyte, Neutrophil, Eosinophil, and Mast Cell Counts
- Remaining Sample Should Be Used for Microbiological, Virological, and/or Malignant Cell Cytology Laboratory Testing, if Indicated
- For Patients with Suspected Interstitial Lung Disease Who Undergo Bronchoalveolar Lavage, Lymphocyte Subset Analysis Should Not Be a Routine Component of Bronchoalveolar Lavage Cellular Analysis
Open Lung Biopsy-Pathologic Patterns
Granulomas (Arch Pathol Lab Med, 2010) [MEDLINE]
- General Comments
- Definition of Granuloma: compact aggregate of histiocytes (macrophages)
- Histiocytes in Granulomas are Often Described as Epithelioid: epithelioid histiocytes have indistinct cell borders and elongated, sole-shaped nuclei (in contrast to the well-defined cell borders and round, oval, or kidney bean–shaped nuclei of ordinary histiocytes
- Aggregation of Histiocytes is the Minimum Requirement for the Diagnosis of a Granuloma: regardless of whether the lesion also contains necrosis, lymphocytes, plasma cells, or multinucleated giant cells
- Definition of Granuloma: compact aggregate of histiocytes (macrophages)
- Infection
- Aspergillus (see Aspergillus, [[Aspergillus]])
- Blastomycosis (see Blastomycosis, [[Blastomycosis]])
- Coccidioidomycosis (see Coccidioidomycosis, [[Coccidioidomycosis]])
- Cryptococcosis (see Cryptococcosis, [[Cryptococcosis]])
- Dirofilariasis (see Dirofilariasis, [[Dirofilariasis]])
- Histoplasmosis (see Histoplasmosis, [[Histoplasmosis]])
- Pneumocystis Jirovecii (see Pneumocystis Jirovecii, [[Pneumocystis Jirovecii]])
- Tuberculosis (see Tuberculosis, [[Tuberculosis]])
- Non-Tuberculous Mycobacteria
- Non-Infectious
- Aspiration Pneumonia (see Aspiration Pneumonia, [[Aspiration Pneumonia]])
- Physiology: due to aspiration of foreign material (vegetable fragments, excipients from oral pills, etc)
- Bronchocentric Granulomatosis (see Bronchocentric Granulomatosis, [[Bronchocentric Granulomatosis]])
- Chronic Berylliosis (see Beryllium, [[Beryllium]])
- Churg-Strauss Syndrome (see Churg-Strauss Syndrome, [[Churg-Strauss Syndrome]])
- Hot Tub Lung (see Myobacterium Avium Complex, [[Myobacterium Avium Complex]])
- Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis (HP) (see Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis, [[Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis]])
- Lymphocytic Interstitial Pneumonia (LIP) (see Lymphocytic Interstitial Pneumonia, [[Lymphocytic Interstitial Pneumonia]])
- Rheumatoid Nodule (see Rheumatoid Arthritis, [[Rheumatoid Arthritis]])
- Sarcoidosis (see Sarcoidosis, [[Sarcoidosis]])
- Silicosis (see Silicosis, [[Silicosis]])
- Talc/Foreign Body Granulomatosis (see Foreign Body Granulomatosis, [[Foreign Body Granulomatosis]])
- Wegener’s Granulomatosis (see Wegeners Granulomatosis, [[Wegeners Granulomatosis]])
- Aspiration Pneumonia (see Aspiration Pneumonia, [[Aspiration Pneumonia]])
Diffuse Alveolar Damage (DAD)
- Acute Interstitial Pneumonia (AIP) (see Acute Interstitial Pneumonia, [[Acute Interstitial Pneumonia]])
- Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) (see Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome, [[Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome]])
- Aspiration Pneumonia (see Aspiration Pneumonia, [[Aspiration Pneumonia]])
- *Drugs: cytotoxic agents, chemotherapy, antibiotics
- Massive Transfusion
- Pneumonia: viral, bacterial, Pneumocystis Jirovecii
- Sepsis (see Sepsis, [[Sepsis]])
- Trauma
- Connective Tissue Disease
- Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF) (see Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis, [[Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis]])
- Radiation Therapy/Radiation Pneumonitis (see Radiation Therapy, [[Radiation Therapy]] and Radiation Pneumonitis and Fibrosis, [[Radiation Pneumonitis and Fibrosis]])
- Toxic Inhalation
- Heavy Metal Fumes
- Cadmium (see Cadmium, [[Cadmium]])
- Mercury (see Mercury, [[Mercury]])
- Nickel Carbonyl (see Nickel Carbonyl, [[Nickel Carbonyl]])
- Ozone (see Ozone, [[Ozone]])
- Smoke Inhalation (see Smoke Inhalation, [[Smoke Inhalation]])
- Heavy Metal Fumes
Organizing Pneumonia
- Cryptogenic Organizing Pneumonia (see [[Cryptogenic Organizing Pneumonia]])
- Organizing Stage of Diffuse Alveolar Damage
- [[Diffuse Alveolar Hemorrhage]]
- Drugs: [[Amiodarone]], Cocaine
- Infections
- Connective Tissue Disease
- Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis (HP) (see Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis, [[Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis]])
- Eosinophilic Pneumonia
- [[Wegeners Granulomatosis]]
Desquamative Interstitial Pneumonia
- Tobacco Abuse
- Idiopathic Desquamative Interstitial Pneumonia
- Connective Tissue Disease
- Eosinophilic Granuloma
- Asbestosis
- Hard Metal Pneumoconiosis (Cobalt)
- Gauchers Disease
- Niemann-Pick Disease
- Hermansky-Pudlak Syndrome
- Drugs: amiodarone, nitrofurantoin
Non-Specific Interstitial Pneumonitis
- Connective Tissue Disease
- Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis (see [[Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis]])
- Diffuse Alveolar Damage
- Infection
- Lymphocytic Interstitial Pneumonia
- HIV Disease (see [[HIV Disease]])
- Infection
- Chronic Eosinophilic Pneumonia
- Idiopathic Pulmonary Hemosiderosis
- Pulmonary Alveolar Proteinosis
- Idiopathic Non-Specific Interstitial Pneumonitis
Usual Interstitial Pneumonia
- Connective Tissue Disease: uncommon
- Asbestosis
- Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis (HP) (see Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis, [[Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis]])
- Chronic Aspiration Pneumonia
- Radiation Pneumonitis
- Hermansky-Pudlak Syndrome
- Neurofibromatosis
- Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF) (see Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis, [[Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis]])
Lymphocytic Interstitial Pneumonia (LIP) (see Lymphocytic Interstitial Pneumonia, [[Lymphocytic Interstitial Pneumonia]])
- Dysproteinemia
- Hypogammaglobulinemia
- Monoclonal or Polyclonal Gammopathy
- Autoimmune
- [[Sjogrens Syndrome]]
- Chronic Active Hepatitis
- [[Myasthenia Gravis]]
- [[Primary Biliary Cirrhosis]]
- [[Hashimotos Thyroiditis]]
- [[Pernicious Anemia]]
- Autoimmune [[Hemolytic Anemia]]
- [[SLE]]
- Allogeneic Bone Marrow Transplant
- Infection
- [[HIV Disease]]
- EBV
- HTLV-1
- [[Tuberculosis]]
- Following [[Legionellosis]]
- Celiac Sprue
- [[Dilantin]]
- Surfactant Protein C Deficiency
- Idiopathic Lymphocytic Interstitial Pneumonia
Eosinophilic Pneumonia
- See Pulmonary Infiltrates with Eosinophilia, [[Pulmonary Infiltrates with Eosinophilia]])
Alveolar Proteinosis
- See Pulmonary Alveolar Proteinosis, [[Pulmonary Alveolar Proteinosis]])
Amyloid Deposition
- See Amyloidosis, [[Amyloidosis]])
Diffuse Alveolar Hemorrhage (DAH)
- See Diffuse Alveolar Hemorrhage, [[Diffuse Alveolar Hemorrhage]])
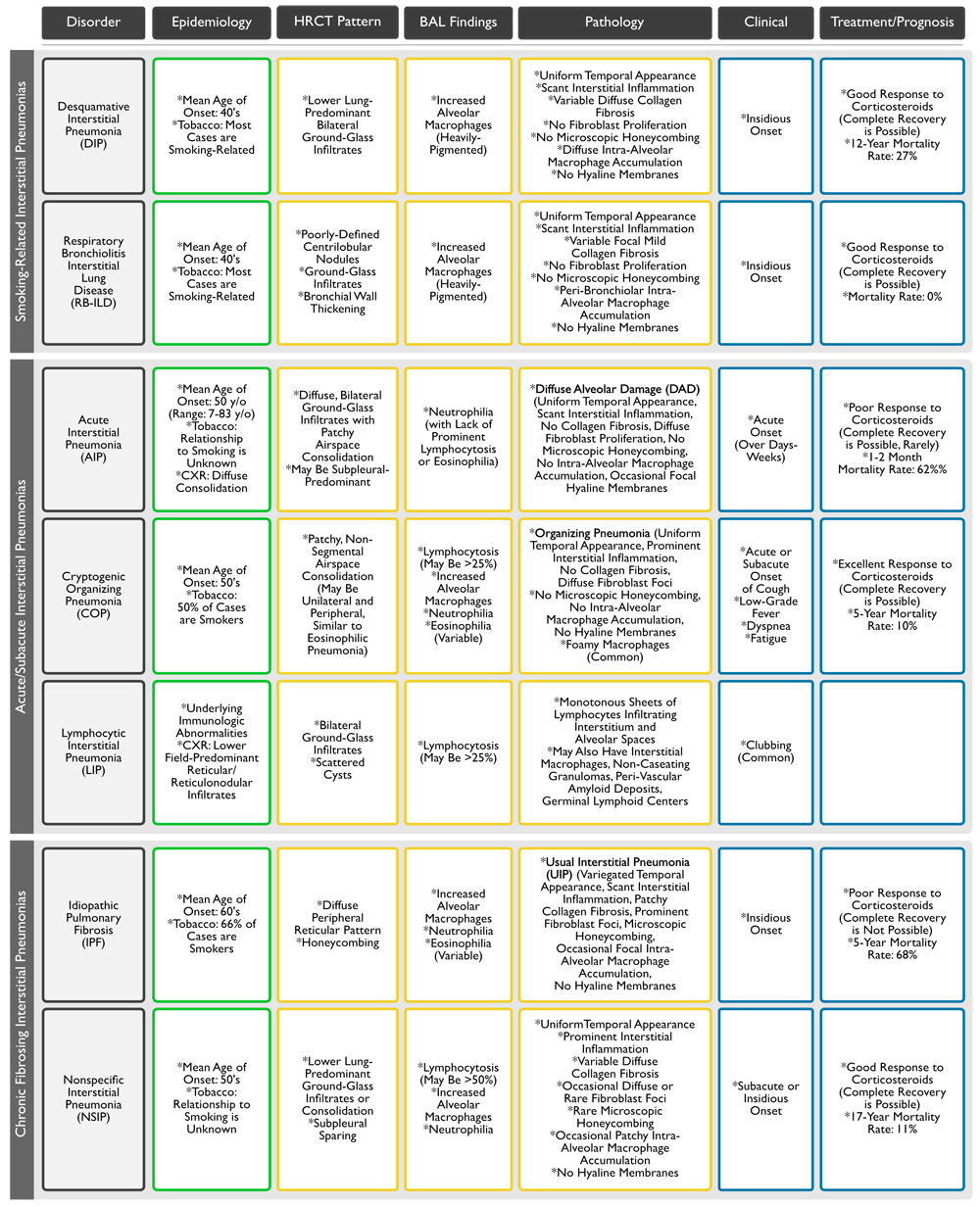
Summary of Features of the Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonias (American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society, 2013) (Am J Respir Crit Care Med, 2013) [MEDLINE]
Clinical Manifestations
Historical Elements
- Age
- Peak age group for connective-tissue associated ILD/LAM/EG/Familial [[Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis]]/Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome/Gaucher’s disease: between age 20-40 y/o
- Peak age group for [[Sarcoidosis]]: 21-30 y/o (almost all cases occur in <60 y/o group)
- Peak age group for [[Eosinophilic Granuloma]]: 20-40 y/o (almost all cases occur in <60 y/o group)
- Peak age group for [[Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis]]: 61-70 y/o (most cases are >50 y/o)
- Gender
- LAM/TS-associated ILD occur exclusively in premenopausal women
- Female-predominance: LIP/Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome/connective tissue-associated ILD (except RA-associated ILD)
- Male predominance: RA-associated ILD/pneumoconioses (due to increased occupational exposure in men)
- Smoking History
- Higher frequency in current or former smokers: EG/DIP/IPF/RB-ILD
- Smoking increases risk of of DAH in Goodpasture’s (smoking exposes BM to Ab)
- Higher frequency in former or never smokers: sarcoidosis/HP
- Duration of Illness
- Acute (days-wks): AIP/AEP/HP/BOOP
- Subacute (wks-months): sarcoidosis/some drug-induced ILD/DAH/idiopathic BOOP/SLE or polymyositis-associated ILD
- Chronic (months-yrs): IPF/sarcoidosis/EG
- Prior Medication Use
- See etiologies
- Family History
- Autosomal-dominant: IPF/sarcoidosis/TS/neurofibromatosis
- Autosomal-recessive: Niemann-Pick/Gaucher’s/Hermansky-Pudlak
- Occupational History
- Especially relation of symptoms to presence in workplace
- Environmental Exposures
- Exposures to pets (especially birds)/air conditioners/humidifiers/hot tubs/evaporative cooling systems (swamp coolers)/areas of water damage
- Familial passive exposure: can occur with asbestos or berylium dust from worker’s clothing
- Spontaneous Pneumothorax (see xxxx, [[xxxx]])
- Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis (see Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis, [[Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis]])
- Lymphangioleiomyomatosis (LAM) (see xxxx, [[xxxx]])
- Neurofibromatosis (see xxxx, [[xxxx]])
- Tuberous Sclerosis (see xxxx, [[xxxx]])
- Cough: usually dry
- Sarcoidosis (see Sarcoidosis, [[Sarcoidosis]])
- BO with or without OP
- Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis (see Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis, [[Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis]])
- Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis (HP) (see Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis, [[Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis]])
- Lipoid Pneumonia
- Lymphangitic Carcinomatosis
- Hemoptysis
- LAM
- TS
- Pulmonary VOD
- DAH syndromes
- Long-standing mitral valve disease
- Wheezing: unusual
- Sarcoidosis (see Sarcoidosis, [[Sarcoidosis]])
- LAM
- Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis (see Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis, [[Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis]])
- Toluene Diisocyanate (TDI)
- Lymphangitic Carcinomatosis
- Chronic Eosinophilic Pneumonia
- Churg-Strauss
- RB-ILD
- Chest Pain
- Sarcoidosis (substernal pain is common)
- SLE-associated ILD (pleuritic)
- RA-associated ILD (pleuritic)
- MCTD-associated ILD (pleuritic)
- Symptoms Preceding Onset of a Connective Tissue Disease
- ILD may precede other manifestations of disease by months-yrs in SLE/RA/polymyositis
Pulmonary Exam Elements
- Velcro Crackles: common
- Late Inspiratory Squeaks: frequent in bronchiolitis
Extrapulmonary Findings
- Clubbing
- [[Asbestosis]] (common)
- Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF) (see Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis, [[Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis]]): common
- [[Sarcoidosis]] (rare)
- Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis (HP) (see Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis, [[Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis]]): rare
- [[Eosinophilic Granuloma]] (rare)
- Hypertension
- Connective tissue diseases
- Some DAH syndromes
- Neurofibromatosis
- Pulmonary Hypertension
- Scleroderma
- Lymphadenopathy (see xxxx, [[xxxx]])
- Sarcoidosis
- Lymphocytic Interstitial Pneumonia (LIP) (see Lymphocytic Interstitial Pneumonia, [[Lymphocytic Interstitial Pneumonia]])
- Lymphoma
- Lymphangitic carcinomatosis
- Hepatosplenomegaly
- Sarcoidosis
- EG
- Connective tissue diseases
- Amyloidosis
- Lymphocytic Interstitial Pneumonia (LIP) (see Lymphocytic Interstitial Pneumonia, [[Lymphocytic Interstitial Pneumonia]])
- Pericarditis (see xxxx, [[xxxx]])
- Radiation pneumonitis
- Connective tissue diseases
- Myositis
- Polymyositis
- Connective tissue diseases
- L-tryptophan
- Muscle Weakness
- Connective tissue diseases
- Uveitis
- Sarcoidosis
- Ankylosing spondylitis
- Behcet’s
- Scleritis
- SLE
- Scleroderma
- Sarcoidosis
- Systemic vasculitides
- Keratoconjunctivitis Sicca (Sjogren’s)
- Lymphocytic Interstitial Pneumonia (LIP) (see Lymphocytic Interstitial Pneumonia, [[Lymphocytic Interstitial Pneumonia]])/Pseudolymphoma
- Primary Pulmonary Lymphoma (MALT)
- Rash-Erythema Nodosum
- Sarcoidosis
- Behcet’s
- Connective tissue diseases
- Histo
- Cocci
- Rash-Maculopapular
- Drug-induced
- Amyloidosis
- Lipoidosis
- Connective tissue diseases
- Gaucher’s
- Rash-Heliotrope
- Dermatomyositis
- Rash-Telangiectasia
- Scleroderma
- Rash-Cutaneous Vasculitis
- Systemic vasculitides
- Connective tissue diseases
- Raynaud’s
- Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF) (see Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis, [[Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis]])
- Scleroderma
- Cafe-au-lait Spots
- [[Neurofibromatosis]]
- Subcutaneous Nodules
- Neurofibromatosis
- [[Rheumatoid Arthritis]]
- Albinism
- Hermansky-Pudlak
- Calcinosis
- Dermatomyositis
- Scleroderma
- Salivary Gland Enlargement
- Sarcoidosis (see Sarcoidosis, [[Sarcoidosis]])
- Lymphocytic Interstitial Pneumonia (LIP) (see Lymphocytic Interstitial Pneumonia, [[Lymphocytic Interstitial Pneumonia]])
References
-
Granulomatous lung disease: an approach to the differential diagnosis. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2010 May;134(5):667-90. doi: 10.1043/1543-2165-134.5.667 [MEDLINE]
-
An Official American Thoracic Society Clinical Practice Guideline: The Clinical Utility of Bronchoalveolar Lavage Cellular Analysis in Interstitial Lung Disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2012 May 1;185(9):1004-14. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201202-0320ST [MEDLINE]
-
An Official American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society Statement: Update of the International Multidisciplinary Classification of the Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonias. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2013 Sep 15;188(6):733-48. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201308-1483ST [MEDLINE]