Indications
- Evaluation of Dyspnea (see Dyspnea)
- Pre-Operative Evaluation
Technique
Flow-Volume Loop
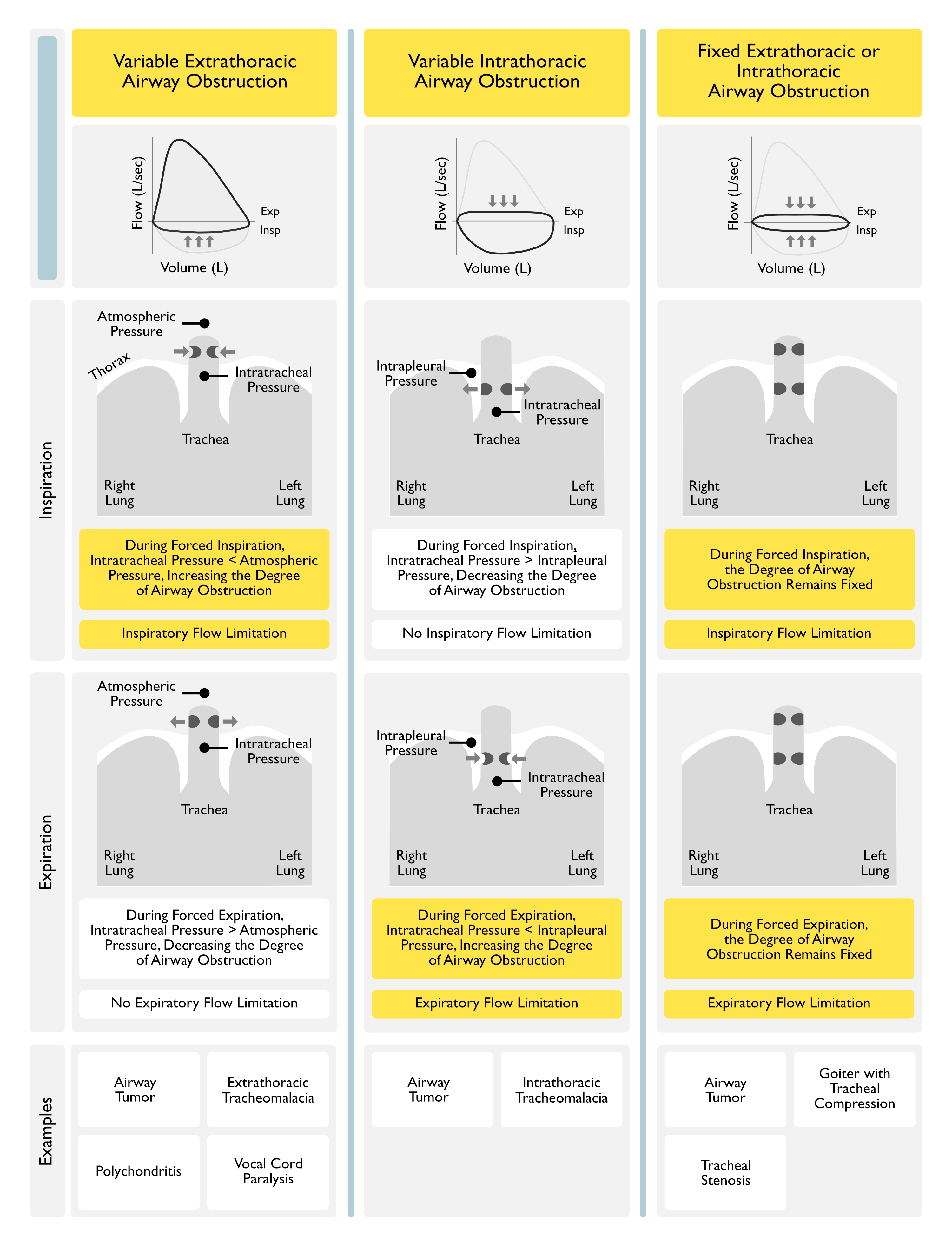
- Variable Extrathoracic Upper Airway Obstruction: adversely affects predominantly inspiratory flow (as inspiratory negative intraluminal pressures exacerbate the inspiratory airway narrowing, while expiratory positive intraluminal pressures splints the obstruction open)
- Example: bilateral vocal cord paralysis (see Bilateral Vocal Fold Immobility)
- Inspiratory Stridor with No Expiratory Flow Obstruction
- Example: bilateral vocal cord paralysis (see Bilateral Vocal Fold Immobility)
- Variable Intrathoracic Upper Airway Obstruction: adversely affects predominantly expiratory flow (as inspiratory negative pressures decrease the inspiratory airway narrowing, while expiratory positive intrapleural pressures exacerbate the airway obstruction)
- Example: tracheomalacia (see Tracheobronchomalacia)
- Expiratory Worsening of Airway Flow Obstruction
- Example: tracheomalacia (see Tracheobronchomalacia)
- Fixed Upper Airway Obstruction: adversely affects both inspiratory and expiratory flows
Use of Predicted Value Equations for Interpretation of PFT Data
- Prediction Equations
- Clinical Data
- Comparison of Predictive Values of GLI 2012, NHANES, and European Community for Steel and Coal (ECSC) (Eur Respir J, 2013) [MEDLINE]
- GLI 2012 equations produce similar predicted values for FEV1 and FVC compared with NHANES, but produce larger values than ECSC
- Differences in the lower limit of normal lead to an important increase in the prevalence rate of a low FVC compared to ECSC, and a significant decrease compared to NHANES prediction equations
- Adopting GLI 2012 equations has small effects on the prevalence rate of airway obstruction: GOLD stages 2-4 lead to >20% underdiagnosis of airway obstruction up to the age of 55 years and to 16-23% overdiagnosis in older subjects
- GLI 2012 equations increase the prevalence of a “restrictive spirometric pattern” compared to European Community for Steel and Coal (ECSC) but decrease it compared to NHANES.
- Comparison of Predictive Values of GLI 2012, NHANES, and European Community for Steel and Coal (ECSC) (Eur Respir J, 2013) [MEDLINE]
ABSTRACT The aim of this study was to determine the diagnostic and interpretative consequences of adopting the Global Lungs Initiative (GLI) 2012 spirometric prediction equations. We assessed spirometric records from 17 572 subjects (49.5% females), aged 18-85 years, from hospitals in Australia and Poland. We calculated predicted forced expiratory volume in 1 s (FEV1), forced expiratory volume (FVC), FEV1/FVC and lower limits of normal (LLN) using European Community for Steel and Coal (ECSC), National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) III and GLI 2012 equations. Obstruction was defined as FEV1/FVCLLN and FVC20% underdiagnosis of airway obstruction up to the age of 55 years and to 16-23% overdiagnosis in older subjects. GLI 2012 equations increase the prevalence of a “restrictive spirometric pattern” compared to ECSC but decrease it compared to NHANES.
Spirometry
Forced Expiratory Volume in One Second (FEV1)
- FEV1 Reflects XXXXXXXXXX
- xxxx
- Considerations in Using the FEV1 % Predicted
- FEV1 % Predicted is Not Applicable to the Assessment of Upper Airway Obstruction
- FEV1 % Predicted May Sometimes Fail to Identify the Severity of the Defect, Especially the Very Severe Stage of Disease
- FEV1 % Predicted Correlates Poorly with Symptoms and Prognosis
- Lung Hyperinflation and Expiratory Flow Limitation During Tidal Breathing May Be Useful to Categorize the Severity of Lung Impairment
- Using the FEV1 % Predicted to Assess the Severity of Obstruction (Eur Respir J, 2005) [MEDLINE]
- Mild Obstruction: FEV1 >70% Predicted
- Moderate Obstruction: FEV1 60-69% Predicted
- Moderately Severe Obstruction: FEV1 50-59% Predicted
- Severe Obstruction: FEV1 35-49% Predicted
- Very Severe Obstruction: FEV1 <35% Predicted
Bronchodilator Responsiveness Trial
- Technique
- Test Baseline FEV1
- Administer Albuterol 100 μg x 4 Doses Via a Spacer
- Re-Test FEV1 15 min Later
- Definition of Bronchodilator Responsiveness: defined as increase in FEV1 and/or FVC ≥12% of control and ≥200 mL
- Considerations in Using Bronchodilator Responsiveness Trial
- In the absence of a significant increase in FEV1 and/or FVC, an improvement in lung function parameters within the tidal breathing range, such as increased partial flows and decrease of lung hyperinflation, may explain a decrease in dyspnea
- The lack of a bronchodilator response in the laboratory does not preclude a clinical response to bronchodilator therapy
Forced Vital Capacity (FVC)
- xxxx
Forced Expiratory Volume in One Second (FEV1)/Forced Expiratory Volume (FVC) Ratio
- xxx
Lung Volumes
- Total Lung Capacity (TLC)
- Functional Residual Capacity (FRC)
- Residual Volume (RV)
Diffusion Capacity for Carbon Monoxide (DLCO)
Technique
- xxx
Pulmonary Function Test (PFT) Obstructive Pattern (see Obstructive Lung Disease)
Pulmonary Function Test Features of Obstructive Pattern
- xxx
Etiology of Obstructive Pattern
Upper Airway Obstruction
- Bilateral Vocal Fold Immobility (BVFI) (see Bilateral Vocal Fold Immobility)
- Cricoarytenoid Arthritis (see Cricoarytenoid Arthritis)
- Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) (see Rheumatoid Arthritis)
- Laryngeal Inflammation
- Amyloidosis (see Amyloidosis)
- Sarcoidosis (see Sarcoidosis)
- Wegener’s Granulomatosis (see Wegener’s Granulomatosis)
- Laryngospasm (see Laryngospasm)
- Neurologic Disease/Dysfunction Involving the Vocal Folds
- Altered Mental Status with Inability to Protect Upper Airway
- Paradoxical Vocal Fold Motion (Vocal Cord Dysfunction) (see Paradoxical Vocal Fold Motion)
- Parkinson’s Disease (see Parkinson’s Disease)
- Developmental Abnormality or Neoplasm the Involving Vocal Folds
- Cervical Node Metastases
- Intubation Injury to Vocal Folds
- Mechanical/Iatrogenic Injury to Vocal Folds
- Nasogastric Tube Syndrome (see Nasogastric Tube)
- Radiation Therapy (see Radiation Therapy)
- Surgical Injury to Vocal Folds
- Anterior Cervical Disk Surgery
- Tracheal Surgery
- Cricoarytenoid Arthritis (see Cricoarytenoid Arthritis)
- Other Upper Airway Disease
- Infection
- Croup (see Croup)
- Deep Neck Infection (see Deep Neck Infection)
- Miscellaneous
- Anaphylaxis (see Anaphylaxis)
- Angioedema (see Angioedema)
- Thermal Injury/Burns of Upper Airway (see Smoke Inhalation)
- Infection
Tracheobronchial Airway Obstruction
- Tracheobronchial Infection
- Klebsiella Rhinoscleroma (see Klebsiella Rhinoscleroma)
- Tuberculosis (see Tuberculosis)
- Tracheobronchial Neoplasm
- Primary Tracheobronchial Tumor
- Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma (Cylindroma) (see Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma)
- Lung Cancer (see Lung Cancer)
- Endobronchial Metastases
- Breast Cancer (see Breast Cancer)
- Melanoma (see Melanoma)
- Primary Tracheobronchial Tumor
- Extrinsic Tracheobronchial Compression
- Granulomatous Mediastinitis and Fibrosing Mediastinitis (see Granulomatous Mediastinitis and Fibrosing Mediastinitis)
- Other Tracheobronchial Obstructive Process
- Smoke Inhalation (see Smoke Inhalation)
- Tracheobronchomalacia (see Tracheobronchomalacia)
- Wegener’s Granulomatosis (see Wegener’s Granulomatosis)
Other Airway Obstruction
- Infection
- Scombroid (see Scombroid)
- Drug
- Cytokine Release Syndrome (see Cytokine Release Syndrome)
- Toxin
- Chlorine Gas/Aerosol Inhalation (see Chlorine)
- Pulmonary Infiltrates with Eosinophilia (PIE) (see Pulmonary Infiltrates with Eosinophilia)
- Allergic Bronchopulmonary Aspergillosis (ABPA) (see Allergic Bronchopulmonary Aspergillosis)
- Simple Pulmonary Eosinophilia (Loffler Syndrome) (see Simple Pulmonary Eosinophilia)
- Tropical Pulmonary Eosinophilia (see Tropical Pulmonary Eosinophilia)
- Bronchiolitis Syndrome
- Bronchiolitis (see Bronchiolitis)
- Bronchiolitis Obliterans (BO) (see Bronchiolitis Obliterans)
- Follicular Bronchiolitis (see Follicular Bronchiolitis)
- Diffuse Panbronchiolitis (see Diffuse Panbronchiolitis)
- Other
- Anaphylaxis (see Anaphylaxis)
- Asthma (see Asthma)
- Bronchiectasis (see Bronchiectasis)
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) (see Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease)
- Cystic Fibrosis (CF) (see Cystic Fibrosis)
- Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis (LCH) (see Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis)
- Lymphangioleiomyomatosis (LAM) (see Lymphangioleiomyomatosis)
Pulmonary Function Test Restrictive Pattern
Pulmonary Function Test Features of Restrictive Pattern
- xxx
Etiology of Restrictive Pattern -> P-A-I-N-T-O-P-P-M
Pleural Disease
- PFT Features
- Variable Lung Volumes
- Examples
- Fibrothorax (see Fibrothorax)
- Large Pleural Effusion (see Pleural Effusion-Exudate)
Alveolar Filling Process
- PFT Features
- Proportional Decrease in TLC, FRC, RV, and VC
- Examples
- Cardiogenic Pulmonary Edema (CHF) (see Congestive Heart Failure)
- Pulmonary Alveolar Proteinosis (PAP) (see Pulmonary Alveolar Proteinosis)
Interstitial Lung Disease (ILD)
- PFT Features
- Decreased TLC
- Decreased FRC
- Decreased VC
- Small Decrease in RV
- Examples
- Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF) (see Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis)
- Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis (HP) see Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis)
Neuromuscular Disease
- PFT Features
- Decreased TLC in Pure Inspiratory Weakness, But Not in Pure Expiratory Muscle Weakness (this is one of the cases where restriction can be diagnosed in setting of a normal TLC)
- No Change in FRC in Cases with Both Inspiratory and Expiratory Muscle Weakness
- Examples
- Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) (see Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis)
- Bilateral Diaphragmatic Paralysis (see Bilateral Diaphragmatic Paralysis)
- Guillain-Barre Syndrome (GBS) (see Guillain-Barre Syndrome)
- Muscular Dystrophy
- Myasthenia Gravis (see Myasthenia Gravis)
- Poliomyelitis (see Poliomyelitis)
Thoracic Cage Abnormality
- PFT Features
- Decreased TLC
- Decrease in VC
- Small Decrease in FRC (normal-slightly increased in Ankylosing Spondylitis cases with restricted thoracic cage expansion)
- Examples
- Ankylosing Spondylitis (see Ankylosing Spondylitis): due to costovertebral spondylosis
- Ascites (see Ascites)
- Kyphoscoliosis (see Kyphoscoliosis)
- Polydermatomyositis (see Polydermatomyositis): extensive soft tissue chest wall calcification
- Pregnancy (see Pregnancy)
- Scleroderma (see Scleroderma): skin tightness over chest may restrict thoracic cage expansion
Obesity
- PFT Features
- xxxx
Pulmonary Hypertension
- PFT Features
- Generally Mild Restriction
- Examples
- Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension (CTEPH) (see Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension): restrictive PFT’S are seen in 20% of cases
- Pulmonary Hypertension (see Pulmonary Hypertension)
Poor Cooperation
- PFT Features
- xxxx
Miscellaneous
- Beta Thalassemia Major (see Thalassemias): restriction may occur (for unclear reasons)
- Pulmonary Function Test Defects Correct with Transfusion and Do Not Correlate with the Iron Burden, Blood Counts, or Degree of Hemolysis
Pulmonary Function Test Non-Specific Pattern (Chest, 2009) [MEDLINE] (Chest, 2011) [MEDLINE]
Epidemiology
- Non-Specific PFT Pattern Occurs in Approximately 9.5% of Complete PFT’s (Chest, 2009) [MEDLINE]
- The Term “Small Airways Obstruction Syndrome” Has Also Been Suggested to Describe this Finding (Chest, 1999) [MEDLINE]
Diagnostic Pulmonary Function Test Features of Non-Specific Pattern
- Decreased FEV1 + Decreased FVC + Normal FEV1/FVC Ratio with Normal Total Lung Capacity (TLC)
- Restriction is Suggested, But a Normal TLC Rules Out Restriction
Clinical Features (Chest, 2009) [MEDLINE]
- Approximately 56% of Patients with Non-Specific PFT Pattern Had Airway Hyperresponsiveness (by Clinical Diagnosis of Asthma and/or Positive Bronchodilator or Methacholine Challenge Response)
- Approximately 50% of Patients with Non-Specific Pattern Had BMI ≥30 kg/m2
- In the Obese Patients, 83% of the Females and 50% of the Males Had Airway Hyperresponsiveness
- In Follow-Up PFT Testing, Approximately 66% of Patients Demonstrate this Pattern Reliably Over Time (Chest, 2011) [MEDLINE]
Pulmonary Function Abnormalities in Diffusion Capacity for Carbon Monoxide (DLCO)
Etiology of Increased Diffusion Capacity for Carbon Monoxide (DLCO)
- Diffuse Alveolar Hemorrhage (DAH) (see Diffuse Alveolar Hemorrhage)
- Physiology: due to increased hemoglobin within alveoli
- Asthma (see Asthma)
- Physiology: due to increased pulmonary capillary blood volume
Etiology of Decreased Diffusion Capacity for Carbon Monoxide (DLCO)
- Chronic Cocaine Abuse (see Cocaine)
- Clinical: patient may be asymptomatic
- Obstructive Lung Diseases (see Obstructive Lung Disease)
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) (see Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease)
- Restrictive Lung Diseases
- Interstitial Lung Disease (ILD) (see Interstitial Lung Disease)
- Pulmonary Vascular Disease
- Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension (CTEPH) (see Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension)
- Idiopathic Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (IPAH) (see Idiopathic Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension)
- Other
- *Anemia *(see Anemia)
References
- Small airways obstruction syndrome, Chest 1999; 116:231-233 [MEDLINE]
- Spirometric reference values from a sample of the general U.S. population. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1999 Jan;159(1):179-87 [MEDLINE]
- GOLD Scientific Committee. Global strategy for the diagnosis, management, and prevention of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. NHLBI/WHO Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD) Workshop summary. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2001; 163: 1256–1276
- Standard for the diagnosis and treatment of patients with COPD: a summary of the ATS/ERS position paper. Eur Respir J 2004; 23: 932–946
- Interpretative strategies for lung function tests. Eur Respir J. 2005 Nov;26(5):948-68 [MEDLINE]
- Conditions associated with an abnormal nonspecific pattern of pulmonary function tests. Chest. 2009 Feb;135(2):419-24. doi: 10.1378/chest.08-1235. Epub 2008 Sep 23 [MEDLINE]
- The nonspecific pulmonary function test: longitudinal follow-up and outcomes. Chest. 2011 Apr;139(4):878-86. doi: 10.1378/chest.10-0804. Epub 2010 Aug 19 [MEDLINE]
- Multi-ethnic reference values for spirometry for the 3-95-yr age range: the global lung function 2012 equations. Eur Respir J. 2012 Dec;40(6):1324-43. doi: 10.1183/09031936.00080312. Epub 2012 Jun 27 [MEDLINE]
- Implications of adopting the Global Lungs Initiative 2012 all-age reference equations for spirometry. Eur Respir J. 2013 Oct;42(4):1046-54. doi: 10.1183/09031936.00195512. Epub 2013 Mar 21 [MEDLINE]
