Obtundation-Coma
Definitions
Clinical Patterns of Brain Dysfunction
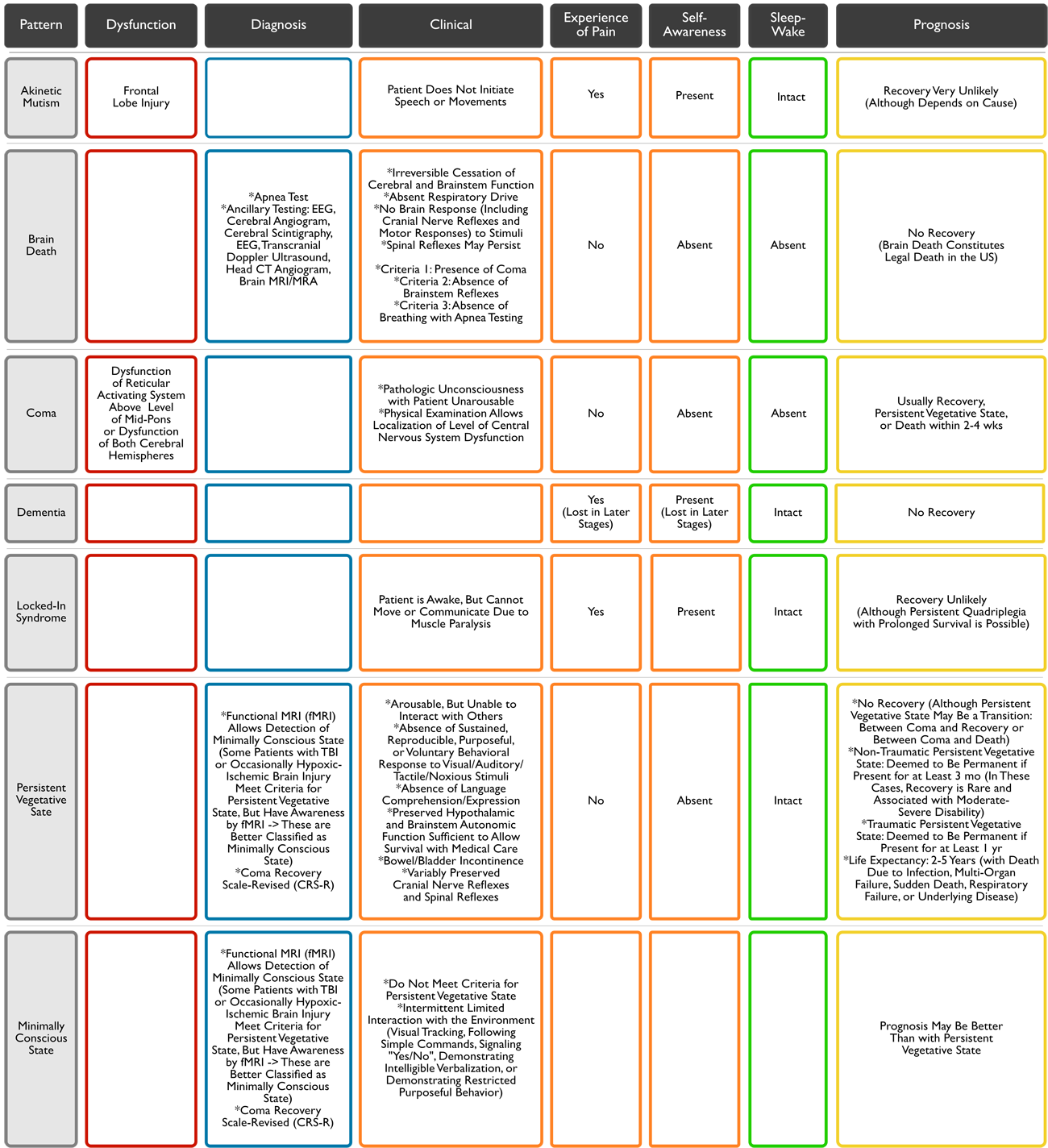
Akinetic Mutism Brain Death (see Brain Death , [[Brain Death]])Coma (see Obtundation-Coma , [[Obtundation-Coma]])Dementia (see Dementia , [[Dementia]])Locked-In Syndrome (see Locked-In Syndrome , [[Locked-In Syndrome]])Persistent Vegetative State : term was first used in 1972Minimally Conscious State
Etiology
Structural
Infection
Metabolic
Central Pontine Myelinolysis (CPM) (see Central Pontine Myelinolysis , [[Central Pontine Myelinolysis]])Hypercalcemia (see Hypercalcemia , [[Hypercalcemia]])Hyperosmolar Hyperglycemic State (HHS) (see Diabetic Ketoacidosis and Hyperosmolar Hyperglycemic State , [[Diabetic Ketoacidosis and Hyperosmolar Hyperglycemic State]]): coma occurs in <20% of casesHypoxemia (see Hypoxemia , [[Hypoxemia]])Lactic Acidosis (see Lactic Acidosis , [[Lactic Acidosis]])Rapid Change in pCO2 During Mechanical Ventilation
Epidemiology : this may particularly occur during the initial mechanical ventilation of a patient with chronic hypercapnia (chronic hypoventilation)Mechanism : rapid shift in arterial pCO2 is almost immediately transmitted throughout the total body water (including the intracellular fluid compartment, the brain, and the cerebrospinal fluid), resulting in potential neurologic injury (it is likely that the rapid change in pCO2 is responsible rather than the alkalosis itself)Clinical
Prevention : maintain pCO2 near patient’s baseline (or gradually decrease the pCO2)
Metabolic Alkalosis (see Metabolic Alkalosis , [[Metabolic Alkalosis]]): with severe metabolic alkalosisxxx xxx xxx xxx xxx
Drug/Toxin
Azacitidine (5-Azacytidine, Vidaza) (see Azacitidine , [[Azacitidine]])Beta Blocker Intoxication (see β-Adrenergic Receptor Antagonists , [[β-Adrenergic Receptor Antagonists]])Carbidopa-Levodopa (Sinemet) (see Carbidopa-Levodopa , [[Carbidopa-Levodopa]])Cefepime (Maxipime) (see Cefepime , [[Cefepime]])Digoxin Intoxication (see Digoxin , [[Digoxin]])Hydrogen Sulfide Gas Inhalation (see Hydrogen Sulfide Gas , [[Hydrogen Sulfide Gas]])Methamphetamine Intoxication (see Methamphetamine , [[Methamphetamine]])Methemoglobinemia (see Methemoglobinemia , [[Methemoglobinemia]])Metoclopramide (Reglan) (see Metoclopramide , [[Metoclopramide]])Nerium Oleander IntoxicationNerium Oleander , [[Nerium Oleander]])Serotonin Syndrome (see Serotonin Syndrome , [[Serotonin Syndrome]])Tricyclic Antidepressant Intoxication (see Tricyclic Antidepressants , [[Tricyclic Antidepressants]])xxx xxx xxx xxx xxx xxx
Other
Leukostasis (see Leukostasis , [[Leukostasis]])xxx xxx xxx xxx xxx xxx xxx xxx
References
CNS Disorder During Mechanical Ventilation in Chronic Pulmonary Disease. JAMA. 1964;189:993 [MEDLINE ]
Property of Kenneth J. Serio, MD. Author is not responsible for errors in content, site is for information purposes only.