Parainfluenza Virus
Epidemiology
Virology
Parainfluenza Virus is a Member of Paramyxovirus Family (see Paramyxoviruses )
Respirovirus Genus: types 1 + 3 Rubulavirus Genus: types 2 + 4
Diagnosis
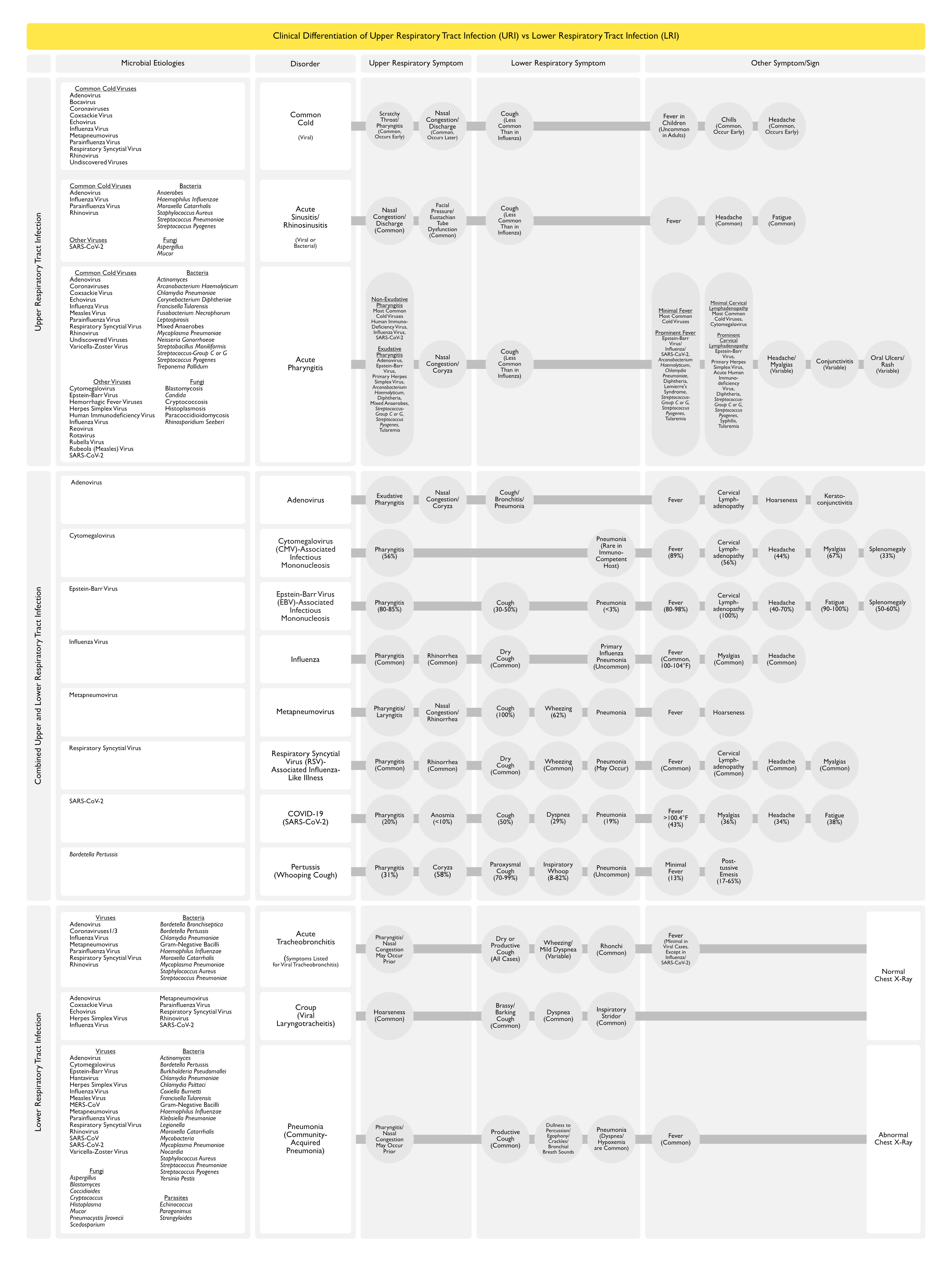
Clinical Differentiation of Upper Respiratory Tract Infection vs Lower Respiratory Tract Infection
Clinical Manifestations
Hematologic Manifestations
Otolaryngologic Manifestations
Acute Rhinosinusitis/Common Cold (see Acute Rhinosinusitis )
Epidemiology : parainfluenza virus/influenza virus/respiratory syncytial virus/adenovirus as a group account for approximately 10-15% of common cold cases
Pulmonary Manifestations
Asthma Exacerbation (see Asthma )
Community-Acquired Pneumonia (see Community-Acquired Pneumonia , [[Community-Acquired Pneumonia]])
Croup (see Croup )
Influenza-Like Illness
Clinical : rapid onset of constitutional symptoms (upper/lower respiratory tract symptoms occur concurrently or after the constitutional symptoms)
Asthenia (see xxxx ): common in second week of illness
Clear Nasal Discharge without Obstruction: common
Dry (Often Persistent) Cough (see xxxx ): predominates later in the first week of illness
Excess Tearing (see xxxx ): common early in the illness
Fatigue (see xxxx ): common in second week of illness
Fever/Chills (see xxxx ): common early in the illness
Peaks to 39-40 degrees C
Lasts for 1-5 days
Headache (see xxxx ): common early in the illness
Mild Conjunctivitis (see xxxx ): common
Mild, Tender Cervical Lymphadenopathy (see xxxx ): common
Myalgias (see xxxx ): common early in the illness
Pain with Eye Movement (see xxxx ): common early in the illness
Pharyngeal Injection/Pharyngitis (see xxxx ): common
Photophobia (see xxxx ): common early in the illness
Treatment
References
General
Property of Kenneth J. Serio, MD. Author is not responsible for errors in content, site is for information purposes only.