Cardiac Physiology
Normal Cardiac Cycle
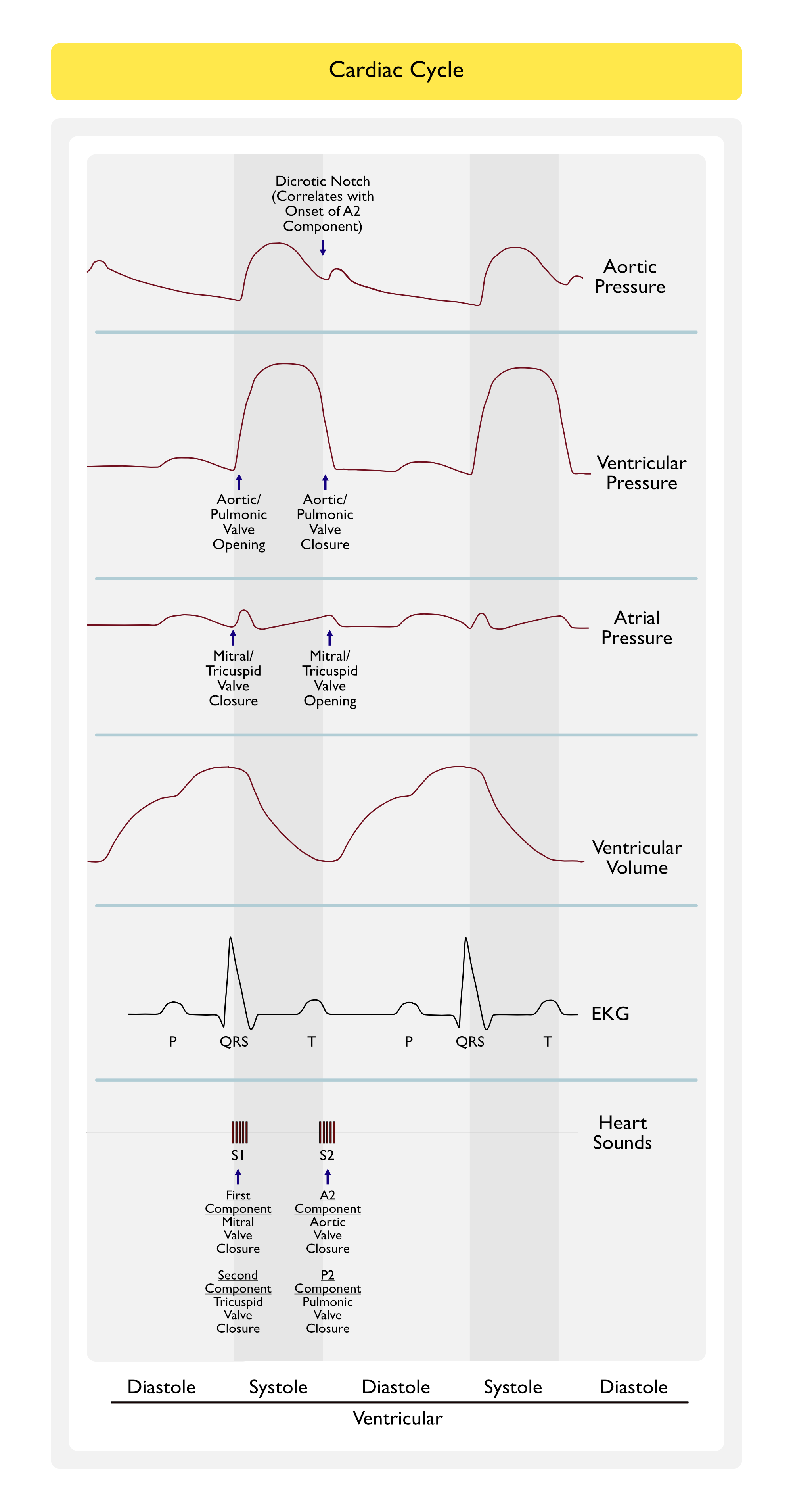
Normal Heart Sounds
Normal Cardiac Conduction
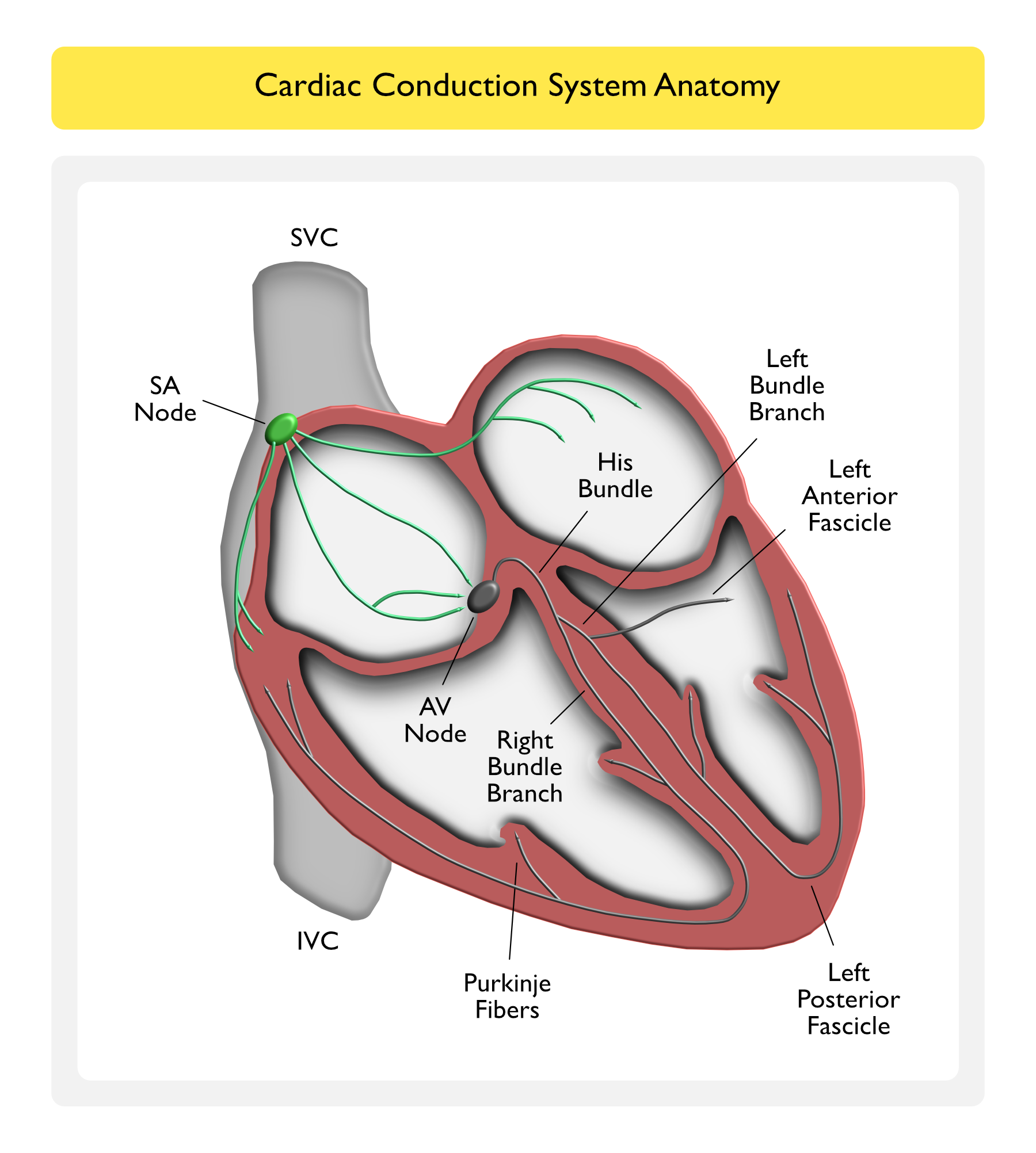
Cardiac Conduction System
Electrical Correlates of the Normal EKG (see Electrocardiogram)
- PR Interval
- Depolarization of Atrium (P-Wave)
- Conduction Through AV Node
- Conduction Through His Bundle
- Conduction Through Bundle Branches
- Conduction Through Fascicles
- Conduction Through Terminal Purkinje Fibers
- QRS
- Ventricular Depolarization
- T-Wave
- Ventricular Repolarization
Blood Supply to the Cardiac Conduction System
- Blood Supply to the Sinoatrial (SA) Node
- Right Coronary Artery: 60% of patients
- Left Circumflex Artery: 40% of patients
- Blood Supply to the Atrioventricular (AV) Node
- Right Coronary Artery: 90% of patients
- Left Circumflex Artery: 10% of patients
- Blood Supply to the His Bundle
- Right Coronary Artery: main blood supply
- Septal Perforators of the Left Anterior Descending Coronary Artery: minor contribution
- Main/Proximal Left Bundle Branch
- Left Anterior Descending Artery: main blood supply
- Right Coronary Artery: collateral flow
- Left Circumflex Artery: collateral flow
- Left Anterior Fascicle
- Septal Perforators of the Left Anterior Descending Coronary Artery: main blood supply
- AV Nodal Artery: 50% of patients
- Left Posterior Fascicle
- Proximal Left Posterior Fascicle
- AV Nodal Artery: main blood supply
- Septal Perforators of the Left Anterior Descending Coronary Artery: in some cases
- Distal Left Posterior Fascicle
- Anterior and Posterior Septal Perforating Arteries (Dual Blood Supply)
- Right Bundle Branch
- Septal Perforators of the Left Anterior Descending Artery: main blood supply
- Right Coronary Artery: some collateral flow (depending on dominance of the system)
- Left Circumflex Artery: some collateral flow (depending on dominance of the system)
References


